Что такое vector3 в unity
Vectors are a fundamental mathematical concept which allow you to describe a direction and magnitude. In games and apps, vectors are often used to describe some of the fundamental properties such as the position of a character, the speed something is moving, or the distance between two objects.
Vector arithmetic is fundamental to many aspects of computer programming such as graphics, physics and animation, and it is useful to understand it in depth to get the most out of Unity.
Vectors can be expressed in multiple dimensions, and Unity provides the Vector2, Vector3 and Vector4 classes for working with 2D, 3D, and 4D vectors. These three types of Vector classes all share many of the same functions, such as magnitude, so most of the information on this page applies to all three types of Vector unless otherwise specified.
This page provides an overview of the Vector classes and their common uses when scripting with them. For an exhaustive reference of every member of the vector classes, see the script reference pages for Vector2, Vector3 and Vector4.
Understanding Vector Arithmetic
Addition
When two vectors are added together, the result is equivalent to taking the original vectors as “steps”, one after the other. Note that the order of the two parameters doesn’t matter, since the result is the same either way.
If the first vector is taken as a point in space then the second can be interpreted as an offset or “jump” from that position. For example, to find a point 5 units above a location on the ground, you could use the following calculation:-
If the vectors represent forces then it is more intuitive to think of them in terms of their direction and magnitude (the magnitude indicates the size of the force). Adding two force vectors results in a new vector equivalent to the combination of the forces. This concept is often useful when applying forces with several separate components acting at once (eg, a rocket being propelled forward may also be affected by a crosswind).
Although the examples here show 2D vectors, the same concept applies to 3D and 4D vectors.
Subtraction
Vector subtraction is most often used to get the direction and distance from one object to another. Note that the order of the two parameters does matter with subtraction:-
As with numbers, adding the negative of a vector is the same as subtracting the positive.
The negative of a vector has the same magnitude as the original and points along the same line but in the exact opposite direction.
Direction and Distance from One Object to Another
If one point in space is subtracted from another, then the result is a vector that “points” from one object to the other:
As well as pointing in the direction of the target object, this vector’s magnitude is equal to the distance between the two positions. You may need a “normalized” vector giving the direction to the target, but with a fixed distance (say for directing a projectile). You can normalize a vector by dividing it by its own magnitude:
This approach is preferable to using both the magnitude and normalized properties separately, since they are both quite CPU-hungry (they both involve calculating a square root).
If you only need to use the distance for comparison (for a proximity check, say) then you can avoid the magnitude calculation altogether. The sqrMagnitude property gives the square of the magnitude value, and is calculated like the magnitude but without the time-consuming square root operation. Rather than compare the magnitude against a known distance, you can compare the squared magnitude against the squared distance:-
This is much more efficient than using the true magnitude in the comparison.
Sometimes, when working in 3D, you might need an “overground heading” to a target. For example, imagine a player standing on the ground who needs to approach a target floating in the air. If you subtract the player’s position from the target’s then the resulting vector will point upwards towards the target. This is not suitable for orienting the player’s transform since they will also point upwards; what is really needed is a vector from the player’s position to the position on the ground directly below the target. You can obtain this by taking the result of the subtraction and setting the Y coordinate to zero:-
Scalar Multiplication and Division
When discussing vectors, it is common to refer to an ordinary number (eg, a float value) as a scalar. The meaning of this is that a scalar only has “scale” or magnitude whereas a vector has both magnitude and direction.
Multiplying a vector by a scalar results in a vector that points in the same direction as the original. However, the new vector’s magnitude is equal to the original magnitude multiplied by the scalar value.
Likewise, scalar division divides the original vector’s magnitude by the scalar.
These operations are useful when the vector represents a movement offset or a force. They allow you to change the magnitude of the vector without affecting its direction.
When any vector is divided by its own magnitude, the result is a vector with a magnitude of 1, which is known as a normalized vector. If a normalized vector is multiplied by a scalar then the magnitude of the result will be equal to that scalar value. This is useful when the direction of a force is constant but the strength is controllable (eg, the force from a car’s wheel always pushes forwards but the power is controlled by the driver).
Dot Product
Below you can see a comparison of how vectors of varying angles compared with a reference vector return a dot product value between 1 and –1 :
The dot product is a mathematically simpler operation than calculating the cosine, so it can be used in place of the Mathf.Cos function or the vector magnitude operation in some circumstances (it doesn’t do exactly the same thing but sometimes the effect is equivalent). However, calculating the dot product function takes much less CPU time and so it can be a valuable optimization.
The dot product is useful if you want to calculate the amount of one vector’s magnitude that lies in the direction of another vector.
Naturally, the direction can be anything you like but the direction vector must always be normalized for this calculation. Not only is the result more correct than the magnitude of the velocity, it also avoids the slow square root operation involved in finding the magnitude.
Cross Product
The cross product is only meaningful for 3D vectors. It takes two 3D vectors as input and returns another 3D vector as its result.
The result vector is perpendicular to the two input vectors. You can use the “right hand screw rule” to remember the direction of the output vector from the ordering of the input vectors. If you can curl your fingers in the order of the input vectors, your thumb points in the direction of the output vector. If the order of the parameters is reversed then the resulting vector will point in the exact opposite direction but will have the same magnitude.
The magnitude of the result is equal to the magnitudes of the input vectors multiplied together and then that value multiplied by the sine of the angle between them. Some useful values of the sine function are shown below:-
The cross product can seem complicated since it combines several useful pieces of information in its return value. However, like the dot product, it is very efficient mathematically and can be used to optimize code that would otherwise depend on slower transcendental functions such as sine and cosine.
Computing a Normal/Perpendicular vector

The “left hand rule” can be used to decide the order in which the two vectors should be passed to the cross product function. As you look down at the top side of the surface (from which the normal will point outwards) the first vector should sweep around clockwise to the second:
The result will point in exactly the opposite direction if the order of the input vectors is reversed.
For meshes, the normal vector must also be normalized. This can be done with the normalized property, but there is another trick which is occasionally useful. You can also normalize the perpendicular vector by dividing it by its magnitude:-
Another useful note is that the area of the triangle is equal to perpLength / 2. This is useful if you need to find the surface area of the whole mesh or want to choose triangles randomly with probability based on their relative areas.
Vector3
struct in UnityEngine
Success!
Thank you for helping us improve the quality of Unity Documentation. Although we cannot accept all submissions, we do read each suggested change from our users and will make updates where applicable.
Submission failed
For some reason your suggested change could not be submitted. Please try again in a few minutes. And thank you for taking the time to help us improve the quality of Unity Documentation.
Description
Representation of 3D vectors and points.
This structure is used throughout Unity to pass 3D positions and directions around. It also contains functions for doing common vector operations.
Besides the functions listed below, other classes can be used to manipulate vectors and points as well. For example the Quaternion and the Matrix4x4 classes are useful for rotating or transforming vectors and points.
Static Properties
Properties
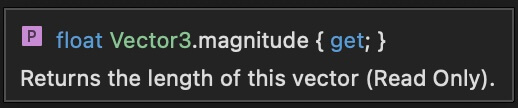
| magnitude | Returns the length of this vector (Read Only). |
| normalized | Returns this vector with a magnitude of 1 (Read Only). |
| sqrMagnitude | Returns the squared length of this vector (Read Only). |
| this[int] | Access the x, y, z components using [0], [1], [2] respectively. |
| x | X component of the vector. |
| y | Y component of the vector. |
| z | Z component of the vector. |
Constructors
Public Methods
| Equals | Returns true if the given vector is exactly equal to this vector. |
| Set | Set x, y and z components of an existing Vector3. |
| ToString | Returns a formatted string for this vector. |
Static Methods
| Angle | Returns the angle in degrees between from and to. |
| ClampMagnitude | Returns a copy of vector with its magnitude clamped to maxLength. |
| Cross | Cross Product of two vectors. |
| Distance | Returns the distance between a and b. |
| Dot | Dot Product of two vectors. |
| Lerp | Linearly interpolates between two points. |
| LerpUnclamped | Linearly interpolates between two vectors. |
| Max | Returns a vector that is made from the largest components of two vectors. |
| Min | Returns a vector that is made from the smallest components of two vectors. |
| MoveTowards | Calculate a position between the points specified by current and target, moving no farther than the distance specified by maxDistanceDelta. |
| Normalize | Makes this vector have a magnitude of 1. |
| OrthoNormalize | Makes vectors normalized and orthogonal to each other. |
| Project | Projects a vector onto another vector. |
| ProjectOnPlane | Projects a vector onto a plane defined by a normal orthogonal to the plane. |
| Reflect | Reflects a vector off the plane defined by a normal. |
| RotateTowards | Rotates a vector current towards target. |
| Scale | Multiplies two vectors component-wise. |
| SignedAngle | Returns the signed angle in degrees between from and to. |
| Slerp | Spherically interpolates between two vectors. |
| SlerpUnclamped | Spherically interpolates between two vectors. |
| SmoothDamp | Gradually changes a vector towards a desired goal over time. |
Operators
Did you find this page useful? Please give it a rating:
Thanks for rating this page!
Is something described here not working as you expect it to? It might be a Known Issue. Please check with the Issue Tracker at
Thanks for letting us know! This page has been marked for review based on your feedback.
If you have time, you can provide more information to help us fix the problem faster.
You’ve told us this page needs code samples. If you’d like to help us further, you could provide a code sample, or tell us about what kind of code sample you’d like to see:
You’ve told us there are code samples on this page which don’t work. If you know how to fix it, or have something better we could use instead, please let us know:
You’ve told us there is information missing from this page. Please tell us more about what’s missing:
You’ve told us there is incorrect information on this page. If you know what we should change to make it correct, please tell us:
You’ve told us this page has unclear or confusing information. Please tell us more about what you found unclear or confusing, or let us know how we could make it clearer:
You’ve told us there is a spelling or grammar error on this page. Please tell us what’s wrong:
You’ve told us this page has a problem. Please tell us more about what’s wrong:
Thanks for helping to make the Unity documentation better!
Is something described here not working as you expect it to? It might be a Known Issue. Please check with the Issue Tracker at issuetracker.unity3d.com.
Copyright © 2020 Unity Technologies. Publication Date: 2021-02-24.
Vector3
struct in UnityEngine
Success!
Thank you for helping us improve the quality of Unity Documentation. Although we cannot accept all submissions, we do read each suggested change from our users and will make updates where applicable.
Submission failed
For some reason your suggested change could not be submitted. Please try again in a few minutes. And thank you for taking the time to help us improve the quality of Unity Documentation.
Description
Representation of 3D vectors and points.
This structure is used throughout Unity to pass 3D positions and directions around. It also contains functions for doing common vector operations.
Besides the functions listed below, other classes can be used to manipulate vectors and points as well. For example the Quaternion and the Matrix4x4 classes are useful for rotating or transforming vectors and points.
Static Properties
Properties
| magnitude | Returns the length of this vector (Read Only). |
| normalized | Returns this vector with a magnitude of 1 (Read Only). |
| sqrMagnitude | Returns the squared length of this vector (Read Only). |
| this[int] | Access the x, y, z components using [0], [1], [2] respectively. |
| x | X component of the vector. |
| y | Y component of the vector. |
| z | Z component of the vector. |
Constructors
Public Methods
| Equals | Returns true if the given vector is exactly equal to this vector. |
| Set | Set x, y and z components of an existing Vector3. |
| ToString | Returns a formatted string for this vector. |
Static Methods
| Angle | Returns the angle in degrees between from and to. |
| ClampMagnitude | Returns a copy of vector with its magnitude clamped to maxLength. |
| Cross | Cross Product of two vectors. |
| Distance | Returns the distance between a and b. |
| Dot | Dot Product of two vectors. |
| Lerp | Linearly interpolates between two points. |
| LerpUnclamped | Linearly interpolates between two vectors. |
| Max | Returns a vector that is made from the largest components of two vectors. |
| Min | Returns a vector that is made from the smallest components of two vectors. |
| MoveTowards | Calculate a position between the points specified by current and target, moving no farther than the distance specified by maxDistanceDelta. |
| Normalize | Makes this vector have a magnitude of 1. |
| OrthoNormalize | Makes vectors normalized and orthogonal to each other. |
| Project | Projects a vector onto another vector. |
| ProjectOnPlane | Projects a vector onto a plane defined by a normal orthogonal to the plane. |
| Reflect | Reflects a vector off the plane defined by a normal. |
| RotateTowards | Rotates a vector current towards target. |
| Scale | Multiplies two vectors component-wise. |
| SignedAngle | Returns the signed angle in degrees between from and to. |
| Slerp | Spherically interpolates between two vectors. |
| SlerpUnclamped | Spherically interpolates between two vectors. |
| SmoothDamp | Gradually changes a vector towards a desired goal over time. |
Operators
Is something described here not working as you expect it to? It might be a Known Issue. Please check with the Issue Tracker at issuetracker.unity3d.com.
Copyright ©2021 Unity Technologies. Publication Date: 2021-12-23.
Vector3 Структура
Определение
Некоторые сведения относятся к предварительной версии продукта, в которую до выпуска могут быть внесены существенные изменения. Майкрософт не предоставляет никаких гарантий, явных или подразумеваемых, относительно приведенных здесь сведений.
Представляет вектор с тремя значениями одинарной точности с плавающей запятой.
Комментарии
Vector3Структура обеспечивает поддержку аппаратного ускорения.
В матричных преобразованиях экземпляры Vector2, Vector3 и Vector4 отображаются в виде строк: вектор v преобразуется матрицей M с помощью умножения vM.
Конструкторы
Создает новый объект Vector3 с тремя элементами, имеющими одинаковое значение.
Создает вектор, элементы которого имеют заданные значения.
Создает новый объект Vector3 на основе заданного объекта Vector2 и значения.
Координата X вектора.
Координата Y вектора.
Координата Z вектора.
Свойства
Получает вектор, три элемента которого равны единице.
Получает вектор (1,0,0).
Получает вектор (1,0,0).
Получает вектор (0,0,1).
Получает вектор, три элемента которого равны нулю.
Методы
Возвращает вектор, элементы которого являются абсолютными значениями каждого из элементов заданного вектора.
Складывает два вектора.
Ограничивает минимальное и максимальное значение вектора.
Копирует элементы вектора в заданный массив.
Копирует элементы вектора в заданный массив, начиная с указанной позиции индекса.
Вычисляет векторное произведение двух векторов.
Вычисляет евклидово расстояние между двумя заданными точками.
Возвращает квадрат евклидова расстояния между двумя заданными точками.
Делит заданный вектор на указанное скалярное значение.
Делит первый вектор на второй.
Возвращает скалярное произведение двух векторов.
Возвращает значение, указывающее, равен ли данный экземпляр указанному объекту.
Возвращает значение, указывающее, равен ли данный экземпляр другому вектору.
Возвращает хэш-код данного экземпляра.
Возвращает длину данного объекта вектора.
Возвращает длину вектора в квадрате.
Выполняет линейную интерполяцию между двумя векторами на основе заданного взвешивания.
Возвращает вектор, элементы которого являются максимальными значениями каждой пары элементов в двух заданных векторах.
Возвращает вектор, элементы которого являются минимальными значениями каждой пары элементов в двух заданных векторах.
Умножает скалярное значение на заданный вектор.
Умножает вектор на заданный скаляр.
Возвращает новый вектор, значения которого являются произведением каждой пары элементов в двух заданных векторах.
Преобразует заданный вектор в отрицательный.
Возвращает вектор с тем же направлением, что и заданный вектор, но с длиной равной единице.
Возвращает отражение вектора от поверхности, которая имеет заданную нормаль.
Возвращает вектор, элементы которого являются квадратным корнем каждого из элементов заданного вектора.
Вычитает второй вектор из первого.
Возвращает строковое представление текущего экземпляра, используя форматирование по умолчанию.
Возвращает строковое представление текущего экземпляра, используя заданную строку форматирования для форматирования отдельных элементов.
Возвращает строковое представление текущего экземпляра, используя заданную строку форматирования для форматирования отдельных элементов и заданный поставщик формата для указания форматирования, определяемого языком и региональными параметрами.
Преобразует вектор посредством заданной матрицы 4×4.
Преобразует вектор посредством заданного значения поворота кватерниона.
Преобразует нормаль вектора посредством заданной матрицы 4×4.
Операторы
Складывает два вектора.
Делит заданный вектор на указанное скалярное значение.
Делит первый вектор на второй.
Возвращает значение, указывающее, равна ли каждая пара элементов в двух заданных векторах.
Возвращает значение, указывающее на неравенство двух заданных векторов.
Умножает скалярное значение на заданный вектор.
Умножает заданный вектор на указанное скалярное значение.
Возвращает новый вектор, значения которого являются произведением каждой пары элементов в двух заданных векторах.
Вычитает второй вектор из первого.
Преобразует заданный вектор в отрицательный.
Методы расширения
Unity Vectors – What Every Game Developer Needs To Know About Vectors In Unity
Help Others Learn Game Development
As soon as you start with Unity game development you will be bombarded with vectors. Most of the time you will use Vector2 for 2D games and Vector3 for 3D games.
So what are vectors and how can we use them?
Definition Of A Vector
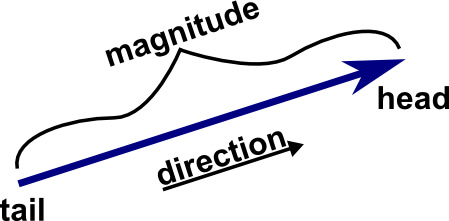
Vectors are a fundamental mathematical concept which allows you to describe a direction and magnitude.
In math, a vector is pictured as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and the arrow is indicating the direction where the vector is going:
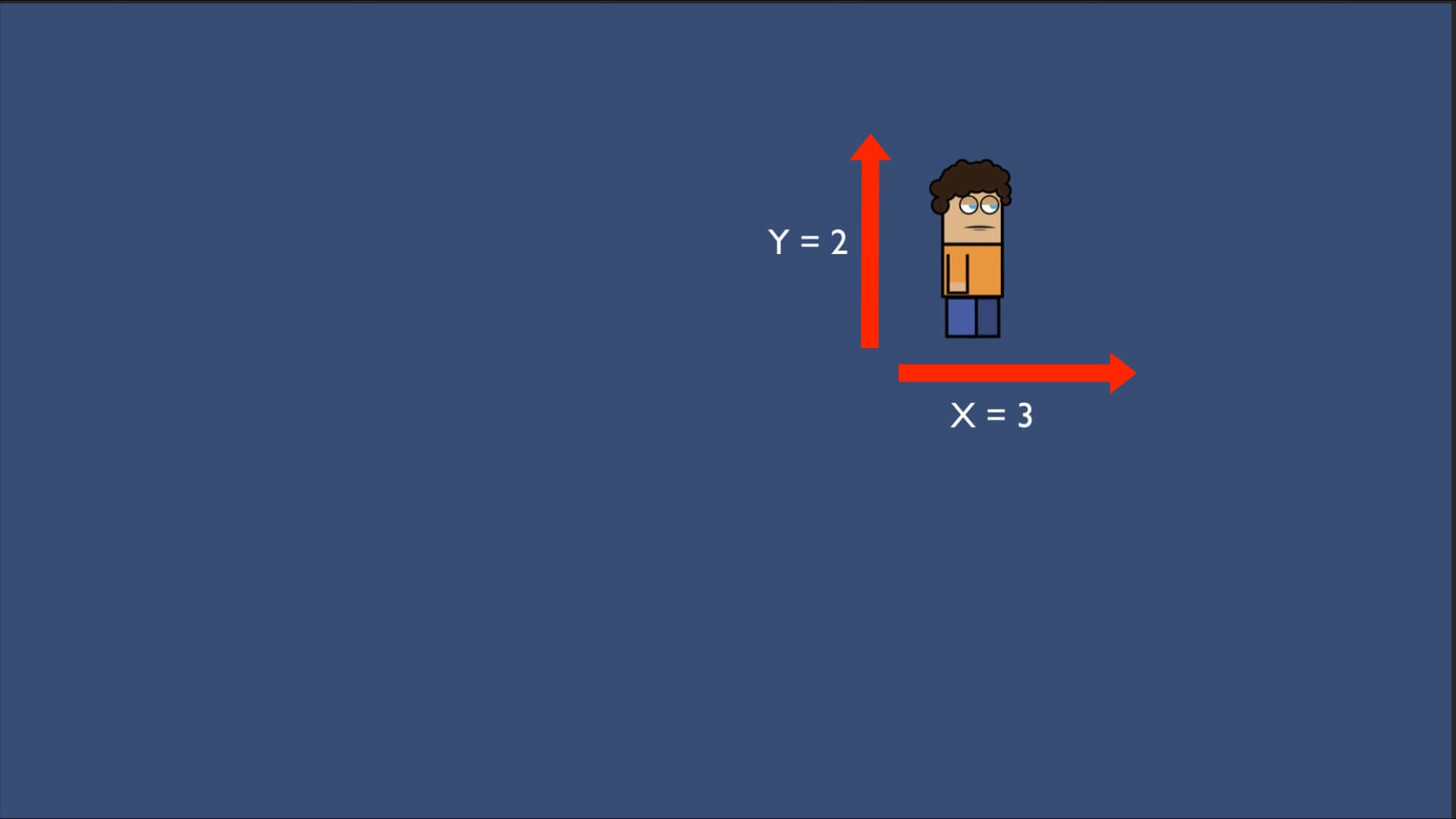
Vector2 And Vector3 In Unity
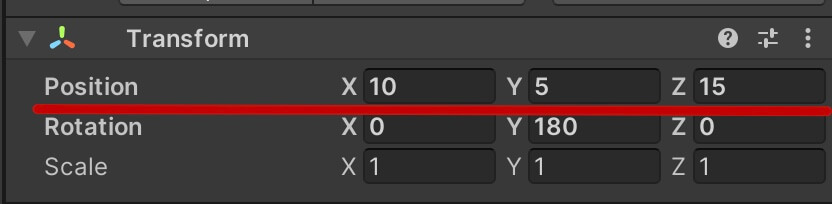
The values for the axis are located in the Position property of the Transform component of course:
The Magnitude Of The Vector
One of the things we use vectors for is to know the magnitude of the game object.
But what is magnitude of a vector?
The magnitude is the distance between the vectors origin (0, 0, 0) and its end point. If we imagine a vector as a straight line, the magnitude is equal to its length as we saw in the first image:
To calculate the magnitude in math, given a position vector → v = ⟨a,b⟩, the magnitude is found by magnitude = √a2 + b2 (square root of a squared + b squared).
In 3D it works the same way, except that we have one more axis in the calculation magnitude = √a2 + b2 + z2 (square root of a squared + b squared + z squared).
But in Unity we simply do this:
For What Do We Use The Magnitude Of A Vector
The magnitude of a vector is used to measure the speed of the vector. I say speed of the vector but its actually the speed of the game object.
For example, if we are moving the game object using its Transform component, we can limit the movement speed using the magnitude of the vector:
Squared Magnitude
One thing that we need to be careful here is that this will calculate the magnitude without using the square root in the operation, which means it will return the magnitude squared e.g. the magnitude will 2x of its actual value.
So if we want to compare a distance between two vectors or the speed of the current vector we need to compare the squared values:
The Direction Of The Vector
One of the most common informations we need in a game is the direction of vectors which indicates in which direction a specific game object is going. This is used to move characters in the game, to create enemy AI and so on.
To get the direction of the vector we need to normalize it, and in Unity we normalize a vector like this:
Using normalized or Normalize will give us the direction of the given vector.
Now you are probably asking what is the difference between the two?
Both lines of code will normalize(return the direction) the given vector, but using normalized on a vector will return a new version of the same vector that we can store in a new variable, and the original version of the vector will stay the same.
Using the Normalize function however, will normalize the vector is self e.g. it will change the original vector.
If you hover over the normalized word in the code you will see the following explanation:
This means that the returned vector has a magnitude of 1 e.g. the length of that vector is 1, because this is how directions are represented in Unity.
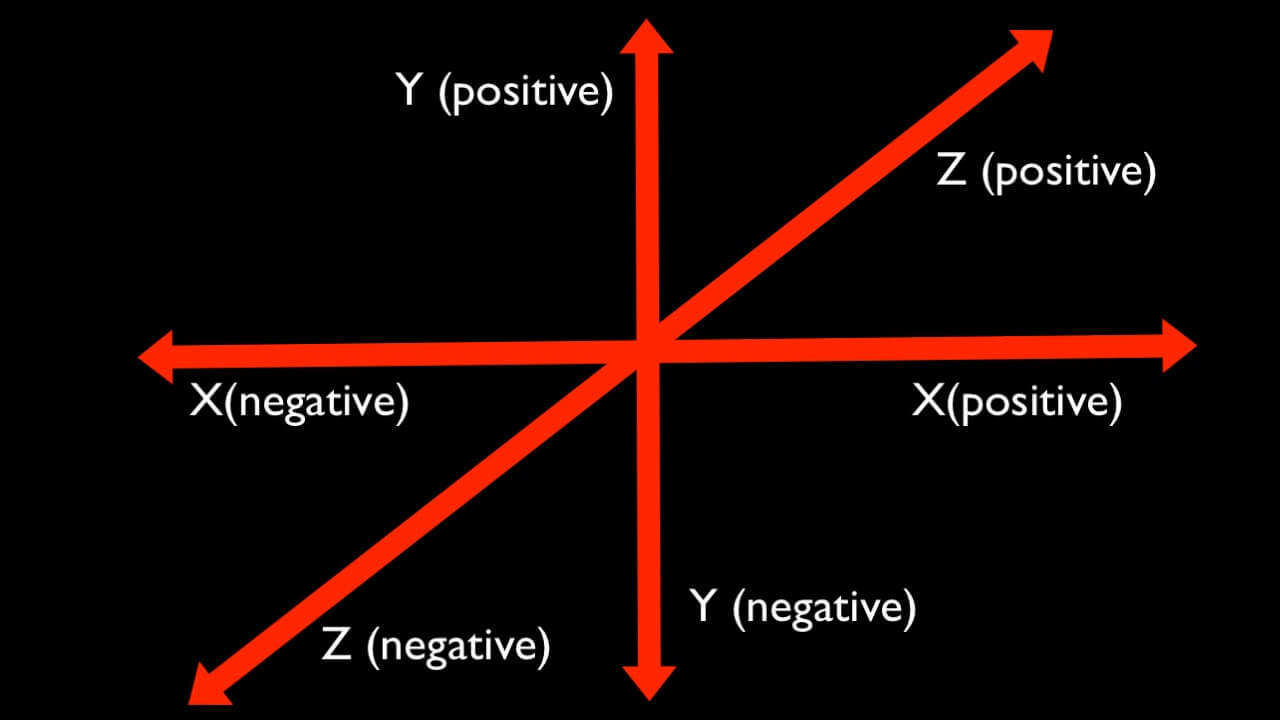
As you can see, X is positive on right side and negative on the left, Y is positive up and negative down, and Z is positive forward and negative backwards.
This is why you see the positive 1 and negative 1 values for the vectors in the code example above.
What Is The Difference Between Vector Magnitude And Vector Normalize
From all the examples we saw so far for the vector’s magnitude and normalization, we can conclude that there is a difference between them and they are both used for different purposes.
The magnitude returns a float, its a single dimensional value expressing vector length. It looses directional information but provides the length information which we can use to control the speed of the vector.
Normalization is a bit of an opposite operation – it returns vector direction, guaranteeing that the magnitude of the resulting vector is one. This means it looses the magnitude information but preserves the direction information which we can use to know where the game object is moving or to move a game object in a specific direction.