Что такое dca prefetch delay
Superfetch
Навигация
Официальный сайт Superfetch
Новости
22 октября, 2018
По просьбе пользователей, мы описали основные причины: Почему зависает или тормозит компьютер, и что с ним делать?
16 октября, 2018
Мы выпустили вторую версию программы superfetch.exe. Теперь можно отключить: SuperFetch, Prefetch, ReadyBoot, это возможно существенно ускорит скорость работы Вашего компьютера!
28 Сентября, 2018
Мы выпустили первую версию программы superfetch 1.00 для быстрого включения/отключения superfetch.
Ждем Ваших отзывов и предложений!
Что такое prefetch и почему его отключают?
Изначально служба prefetch разрабатывалась как отдельный компонент ОС Windows (начиная с ОС Windows XP) для ускорения запуска системы и приложений. Все это было в далеком 2001 году. Представляете конфигурацию компьютеров в те времена?
Теперь вернемся в наш 2018 год.
Проблема кэширования данных уже давно решена на аппаратном уровне и заложена в любой жесткий диск с магнитным накопителем. Где для кэширования данных есть собственная память, объем которой рассчитывается исходя из скорости вращения диска, чтобы соответсвовать максимальной пропускной способности для интерфейсов подключения (IDE, далее SATA и прочие).
Почему надо отключать эту службу? Служба prefetch (в списке служб она называется prefetcher) наблюдает за запуском приложений и создает файлы трассировки оптимизации кода. Эта сложная структура кэша исполняемого кода, которая собирается ограниченное время (10 секунд после запуска) и подставляется в память при повторном запуске приложений. Отключают эту службу потому, что время потраченное на создание трассировки, намного больше, чем время и скорость считывания данных с современных жестких дисков. Тем более появились более быстрые SSD диски.
Microsoft в принудительном порядке отключает prefetch на собственных планшетах линейки Surface.
🛠 Настраиваем и оптимизируем работу SSD-накопителя в Windows и Ubuntu
Miroslav Kungurov
Большая часть рекомендаций по оптимизации работы и продлении жизни SSD-накопителя сводится к уменьшению количества записи и перезаписи. В этой статье разберемся, какие службы ОС нужно включить или отключить, чтобы продлить жизнь накопителя, а какие нет смысла трогать и лучше оставить работать в конфигурации по умолчанию.
Команда TRIM
Память твердотельного накопителя состоит из блоков, а блоки состоят из страниц. Чтобы обновить информацию в странице, нужно стереть весь блок целиком и только потом записать новые данные. Операция удаления не удаляет данные физически, а только помечает их для удаления. При перезаписи блока добавляется дополнительная операция очистки, из-за которой падает скорость операции. Команда TRIM очищает блоки в фоновом режиме, чтобы наготове всегда были свободные и скорость записи оставалась максимальной.
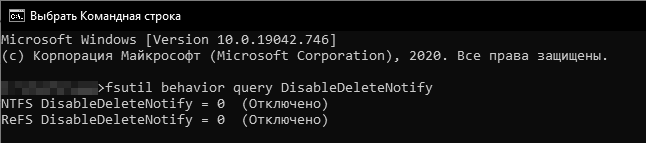
Чтобы определить состояние TRIM в Windows введем в консоли:
DisableDeleteNotify = 1 – TRIM отключен
DisableDeleteNotify = 0 – TRIM включен
Для включения TRIM введем в командной строке:
Для выключения TRIM:
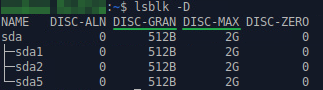
Проверим, включена ли команда TRIM в Ubuntu следующей командой:
Если у столбцов DISC-GRAN и DISC-MAX нулевые значения, то TRIM выключен.
Чтобы запустить TRIM вручную, введем в терминале команду:
Служба SysMain
Служба SysMain (Windows 10) в предыдущих версиях Windows называлась Superfetch. Когда ОЗУ недостаточно, SysMain не записывает данные в файл подкачки, а сжимает их в ОЗУ. Также служба объединяет страницы с одинаковым содержимым. Получаем снижение объема записи на диск. Отключать нет смысла.
Как проверить состояние SysMain:
Служба Prefetcher
Как проверить состояние Prefetch:
Система индексирования Windows
Как отключить индексацию файлов:
Режим гибернации
Режим гибернации сохраняет содержимое оперативной памяти на SSD перед выключением компьютера. При включении данные с SSD загружаются в ОЗУ. Если сверхбыстрый запуск ОС не нужен, а достаточно быстрого запуска с SSD, то гибернацию можно отключить.
Чтобы отключить гибернацию в Windows откроем консоль и введем:
Для включения гибернации используем команду:
Точки восстановления системы
Отключение точек восстановления лишит пользователя возможности восстановить систему. Чем больше места, тем больше точек восстановления имеется в распоряжении. Старые точки восстановления удаляются автоматически, когда все место под них занято и нужно создать новую. Отключать не стоит.
Как проверить состояние точек восстановления:
Быстрый доступ к настройкам восстановления системы:
Служба дефрагментации и автоматического обслуживания
Начиная с Windows 7 система научилась определять тип накопителя и отключает дефрагментацию для SSD, а взамен выполняет TRIM. Как оказалось, не всегда.
Как посмотреть состояние службы дефрагментации:
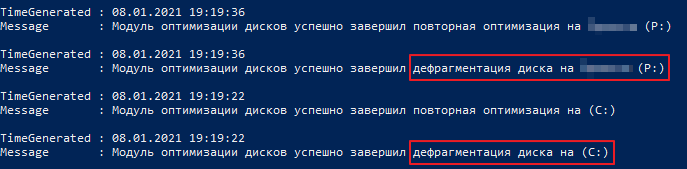
Чтобы посмотреть журнал оптимизации и дефрагментации дисков откроем PowerShell из меню пуск и введем следующую команду:
Мои диски С и P расположены на твердотельных накопителях и Windows почему-то провела дефрагментацию этих дисков. Это связано с тем, что я переустанавливал Windows и это было первое выполнение задачи оптимизации по расписанию. Потом ОС выполняла только оптимизацию дисков.
Файл подкачки
Когда ОЗУ недостаточно, Windows обеспечивает надежную работы программы, перемещая неиспользуемые данные на диск в файл подкачки. При его отключении некоторые программы могут работать некорректно, поэтому рекомендуется выбирать его размер в автоматическом режиме. Если файл подкачки неоправданно велик, то задать его размер вручную.
Настройка файла подкачки:
Выравнивание разделов
Разделы выравнивают, чтобы физические ячейки объема соответствовали логическим ячейкам и сократилось количество дисковых операций. Если разделы отличаются по длине – один кластер перекрывает два блока секторов, как в HDD, – удваивается число операций чтения и записи, накопитель работает медленнее и повышается его износ (рис. 11 ).
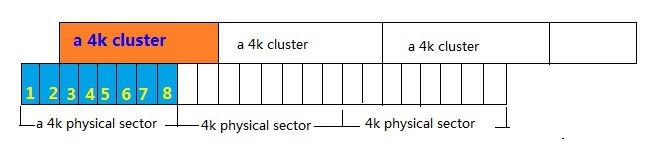
В SSD также нужно выравнивать разделы, чтобы продлить срок службы накопителя.
Чтобы узнать размер кластера в Windows введем в консоли:
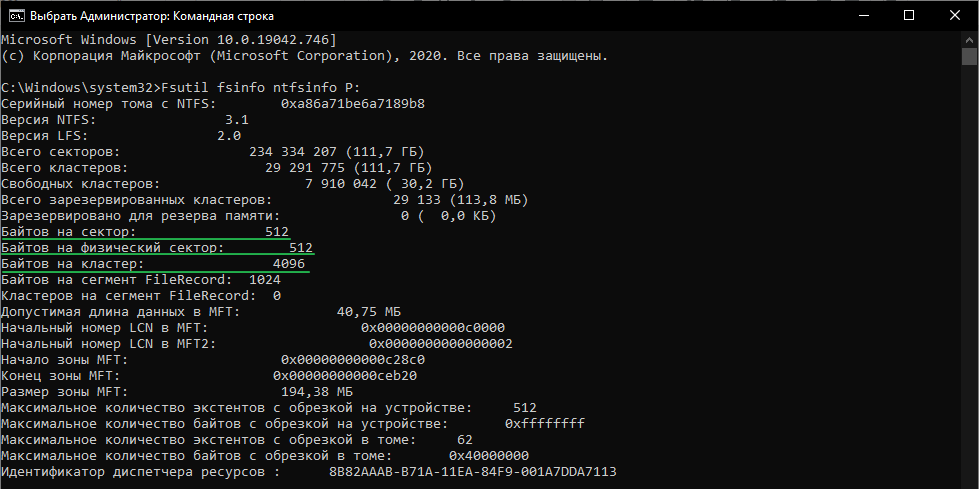
Как изменить размер кластера в Windows:
Как узнать размер кластера в Ubuntu:
/dev/sda1 – путь к разделу.
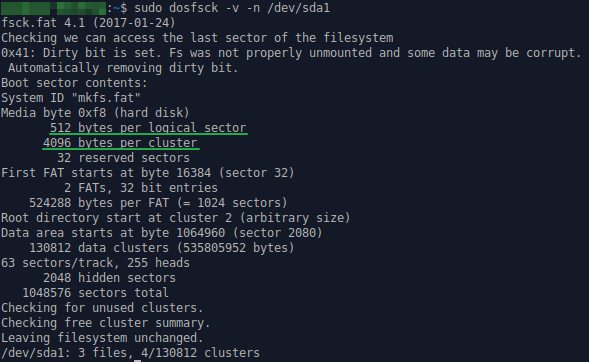
Как изменить размер кластера в Ubuntu (все данные будут удалены):
mkfs.ntfs – форматирование в NTFS ( mkfs.ext4 – форматирование в ext4).
-c – проверка на наличие битых блоков на устройстве.
4096 – размер кластера.
Как узнать выровнен ли раздел в Windows:
Как узнать выровнен ли раздел в Ubuntu:
1 – номер раздела. Например, у sda1 будет единица.

Чтобы узнать номер раздела введем в консоли:
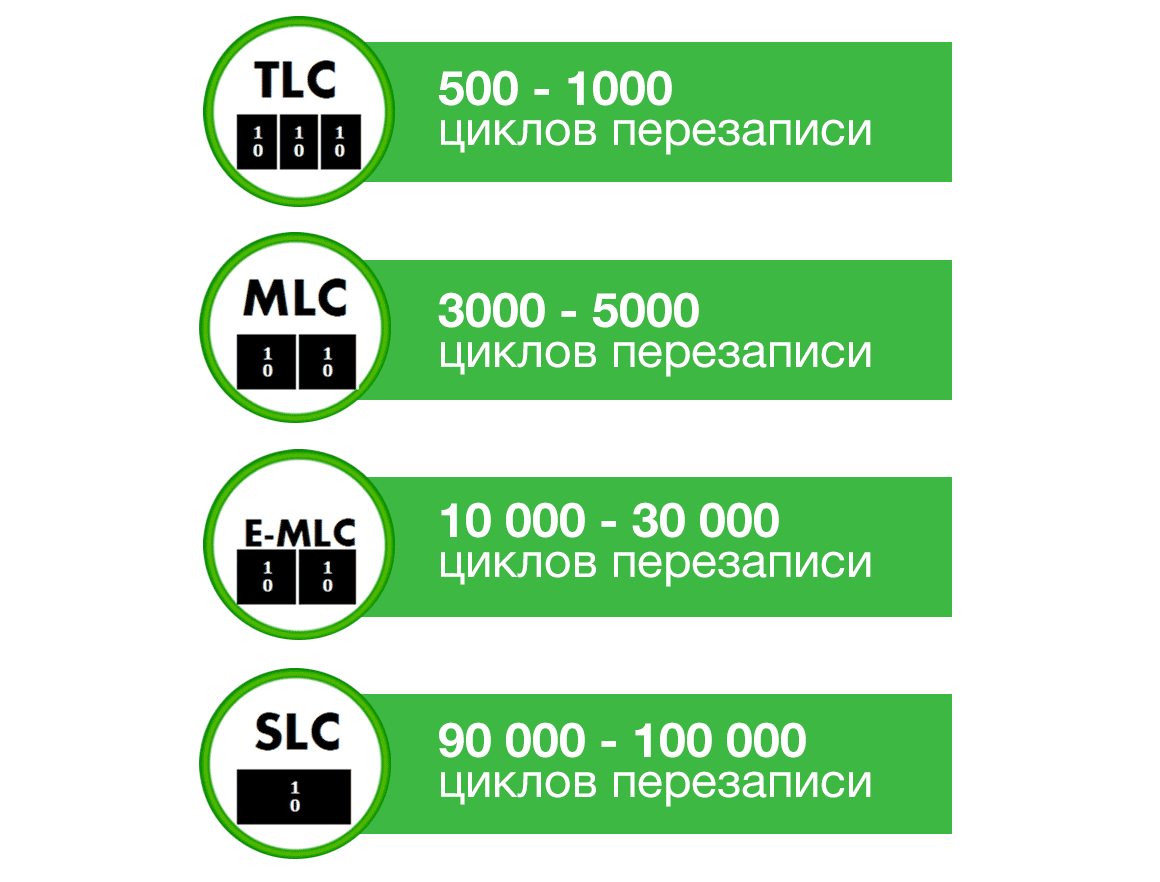
На что смотреть при покупке SSD
У твердотельных дисков есть два параметра, которые определяют его долговечность:
Чем больше значение этих параметров, тем лучше.
Как оптимизировать работу SSD-накопителя
Мы узнали какие службы действительно продлевают жизнь и ускоряют твердотельный накопитель, а какие нет. Про SSD для рядового потребителя можно сказать одно – установил и забыл, так как все важные службы работают в автоматическом режиме, а ненужные отключены.
Dram rapl mode что это
Running Average Power Limit
by Srinivas Pandruvada
RAPL Evolution
The thermal design power (TDP) represents the maximum amount of power the cooling system in a computer is required to dissipate. For example, for a processor with TDP of 35W, Intel guarantees the OEM that if it implements a chassis and cooling system capable of dissipating that much heat, the chip will operate as intended. This is the power budget under which the system needs to operate. But this is not the same as the maximum power the processor can consume. It is possible for the processor to consume more than the TDP power for a short period of time without it being “thermally significant”. Using basic physics, heat will take some time to propagate, so a short burst may not necessarily violate TDP.
Let’s analyze how a TDP can influence performance.
With a single core CPU, an application demanding performance will get full performance, as long as it is under TDP.
If one more core is added, a multi-threaded workload can demand full performance on both cores. If the CPU is using maximum frequency on both cores, this will consume more power than TDP. To avoid this, the CPU will use different maximum frequencies, depending on the number of active cores. So, out of two, if one core is more active than the other, it can use the remaining thermal budget and run at a higher frequency. This is achieved by introduction of turbo mode.
Intel® Turbo boost technology allows processor cores to run faster than their base frequency, if the operating condition permits. A Power Control Unit (PCU) firmware decides based on the:
Once the GPU is added to the package, its power must also be considered in making this turbo boost decision.
The PCU uses some internal models and counters to predict the actual and estimated power consumption. Before Sandy Bridge microarchitecture, turbo decisions are driven by models, which by nature tend to be conservative, to avoid issues in some isolated cases. Sandy Bridge added onboard power meter capability, which can be used to make better decisions, rather than decisions based purely on models. In addition, it exported these power meters and power limits used in its calculations through a set of MSRs (Machine Specific Registers) and PCIe config space. This interface is called the RAPL interface.
RAPL Use Cases
RAPL Power meter capability
RAPL provides a set of counters providing energy and power consumption information. RAPL is not an analog power meter, but rather uses a software power model. This software power model estimates energy usage by using hardware performance counters and I/O models. Based on our measurements, they match actual power measurements [3].
RAPL Power Limiting
RAPL provides a way to set power limits on processor packages and DRAM. This will allow a monitoring and control program to dynamically limit max average power, to match its expected power and cooling budget. In addition, power limits in a rack enable power budgeting across the rack distribution. By dynamically monitoring the feedback of power consumption, power limits can be reassigned based on use and workloads. Because multiple bursts of heavy workloads will eventually cause the ambient temperature to rise, reducing the rate of heat transfer, one uniform power limit can’t be enforced. RAPL provides a way to set short term and longer term averaging windows for power limits. These window sizes and power limits can be adjusted dynamically.
RAPL performance feedback
RAPL counters capture the total time that the RAPL mechanism forced the P-state to be below the OS-requested P-state. Also, it has a counter which tracks the total time that the RAPL power limit limited the operating frequency of the processor. These counters can be used to fine tune or rebalance loads on nodes, if there are performance degradations caused by running below OS-requested P-states.
RAPL Domains
In RAPL, platforms are divided into domains for fine grained reports and control. A RAPL domain is a physically meaningful domain for power management. The specific RAPL domains available in a platform vary across product segments.
Each RAPL domain supports:
The RAPL interface is used in multiple products at OTC. The following list summarizes some of the products and their usages:
TurboStat
TurboStat utility that’s part of the Linux kernel tools and is now capable of displaying the wattage information. This wattage information is read using RAPL MSRs.
PowerTOP
PowerTOP provides estimated power consumption for various components. These estimates are based on: real power measurements, taken using a power meter, and a power model that takes into account estimated activity on that component. RAPL can help get the exact power numbers for CPUs/GPUs and DRAMs to show actual power consumption. Recent changes in PowerTOP show the actual CPU, GPU, and DRAM power consumption.
RAPL driver
The RAPL driver is implemented as a power cap driver. This is available in the latest Linux releases from kernel.org.
Linux Thermal Daemon
RAPL power limits are very effective in reducing package temperature. The Linux thermal daemon uses RAPL interface using RAPL driver to control platform thermals.
По умолчанию все характеристики оперативной памяти компьютера определяются БИОС и Windows полностью автоматически в зависимости от конфигурации оборудования. Но при желании, например, попытке разогнать RAM, есть возможность произвести регулировку параметров самостоятельно в настройках BIOS. К сожалению, сделать это можно не на всех материнских платах, на некоторых старых и простых моделях такой процесс невозможен.
Настраиваем RAM в BIOS
Изменять можно основные характеристики оперативной памяти, то есть тактовую частоту, тайминги и напряжение. Все эти показатели взаимосвязаны. И поэтому к настройке оперативной памяти в БИОС нужно подходить теоретически подготовленным.
Способ 1: Award BIOS
Если на вашей системной плате установлена прошивка от Phoenix/Award, то алгоритм действий будет выглядеть примерно так, как указано ниже. Помните, что названия параметров могут незначительно отличаться.
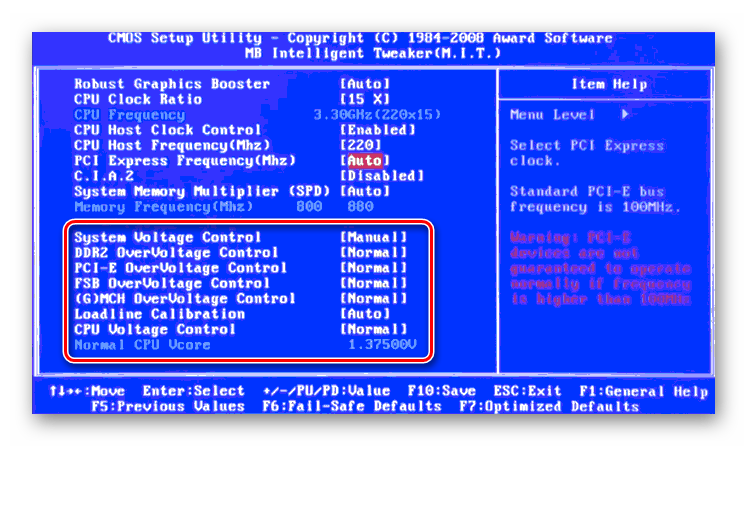
Можно осторожно увеличить напряжение тока, подаваемого на RAM, но не более чем на 0,15 вольта.
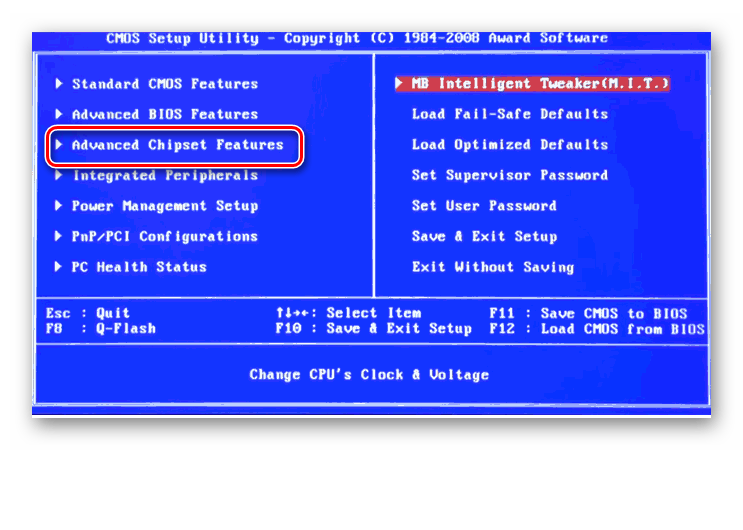
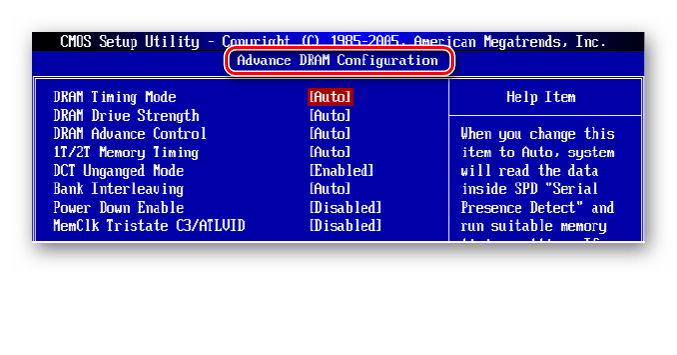
Возвращаемся на главную страницу БИОС и выбираем параметр «Advanced Chipset Features».
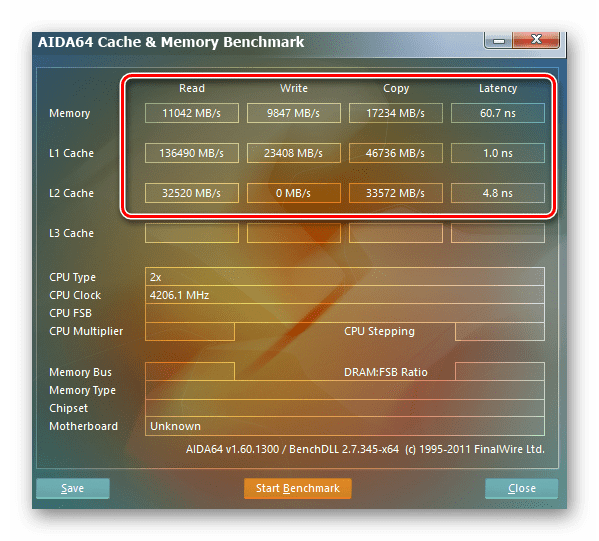
Настройки закончены. Выходим из BIOS с сохранением изменений и запускаем любой специальный тест для проверки стабильности работы системы и RAM, например, в AIDA64.
Способ 2: AMI BIOS
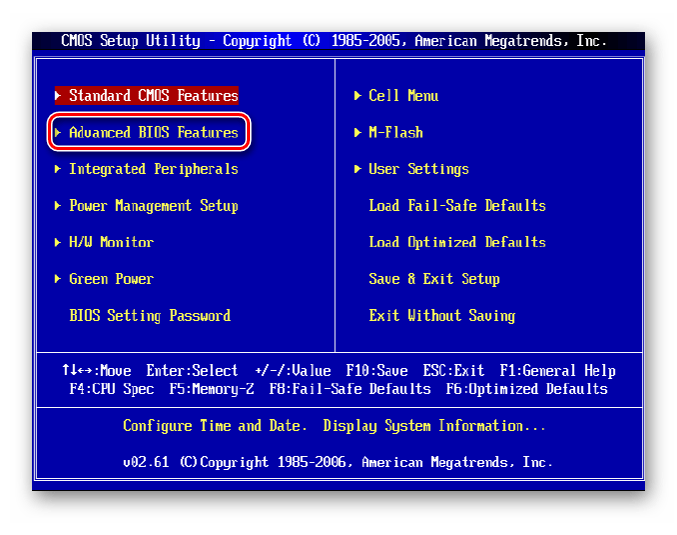
Если БИОС на вашем компьютере от American Megatrends, то кардинально значительных отличий от Award не будет. Но на всякий случай вкратце рассмотрим этот случай.
- Входим в BIOS, в главном меню нам нужен пункт «Advanced BIOS Features».
Способ 3: UEFI BIOS
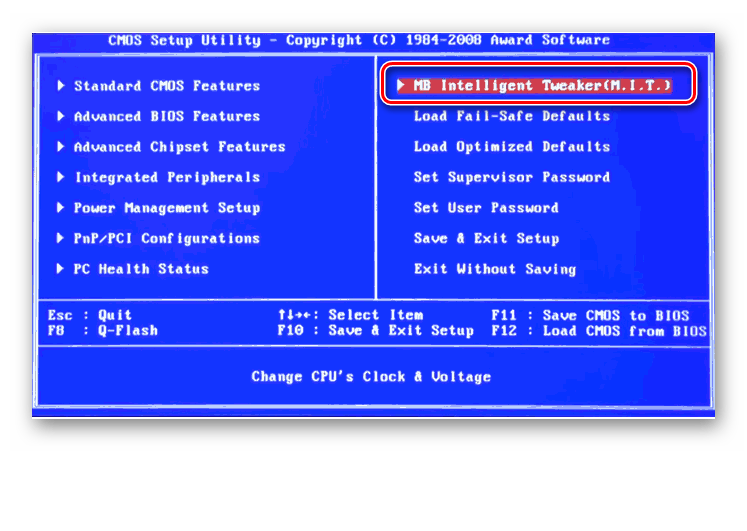
На большинстве современных материнских плат стоит UEFI BIOS с красивым и удобным интерфейсом, поддержкой русского языка и компьютерной мыши. Возможности по настройке RAM в такой прошивке очень широкие. Рассмотрим их подробно.
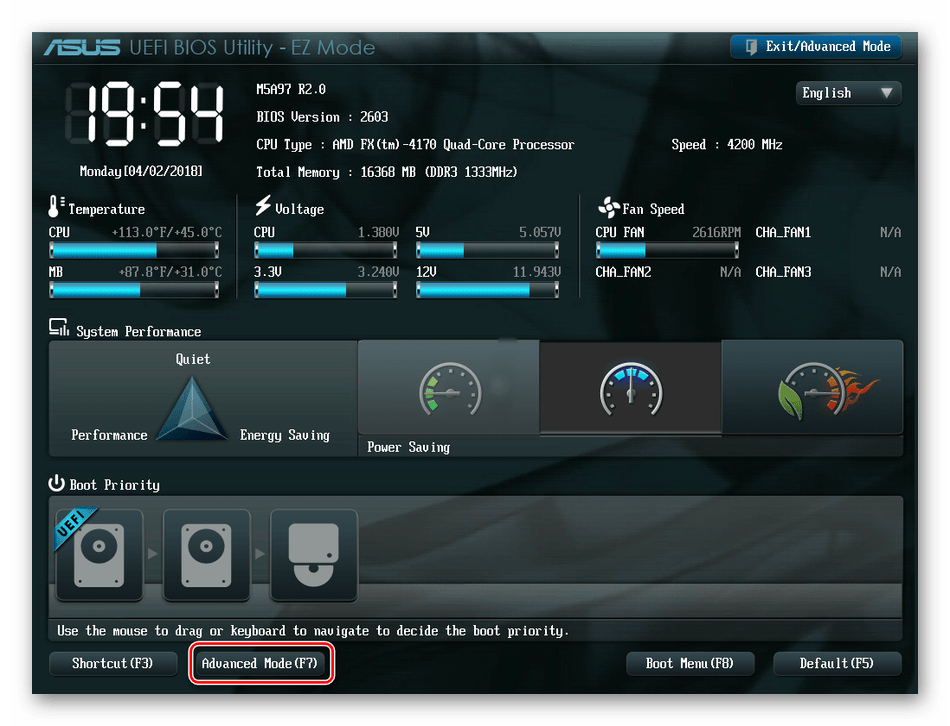
- Заходим в БИОС, нажав Del или F2. Реже встречаются другие сервисные клавиши, узнать их можно в документации или из подсказки внизу экрана. Далее переходим в «Advanced Mode», нажав F7.
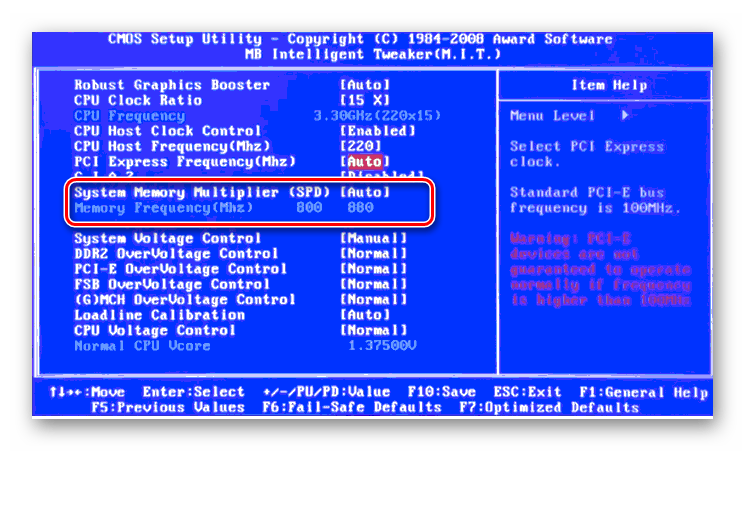
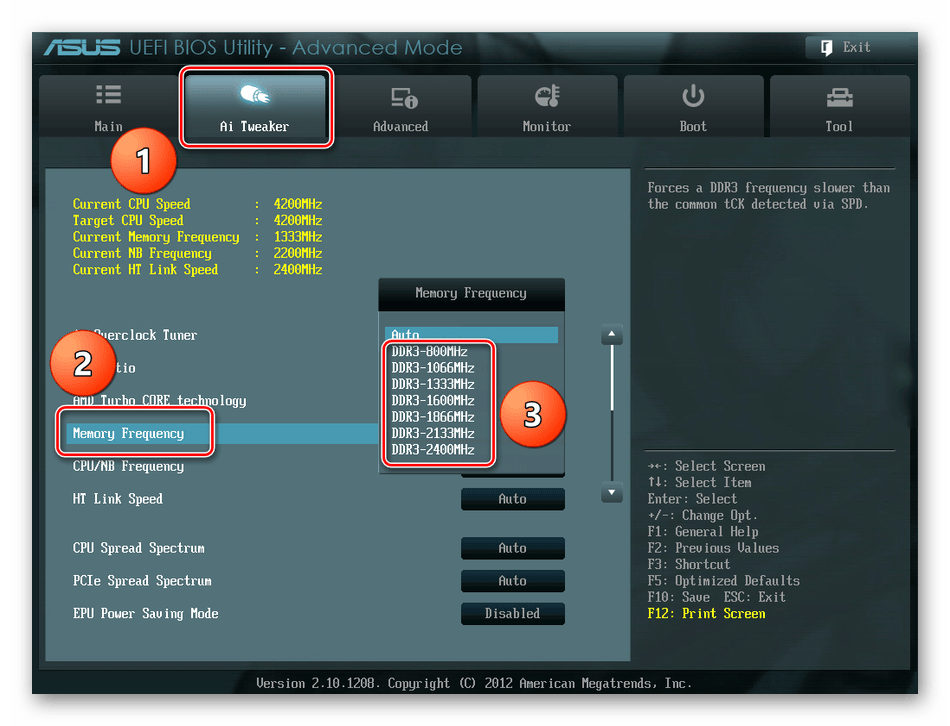
На странице расширенных настроек переходим на вкладку «Ai Tweaker», находим параметр «Memory Frequency» и в выпадающем окне выбираем желаемую тактовую частоту оперативной памяти.
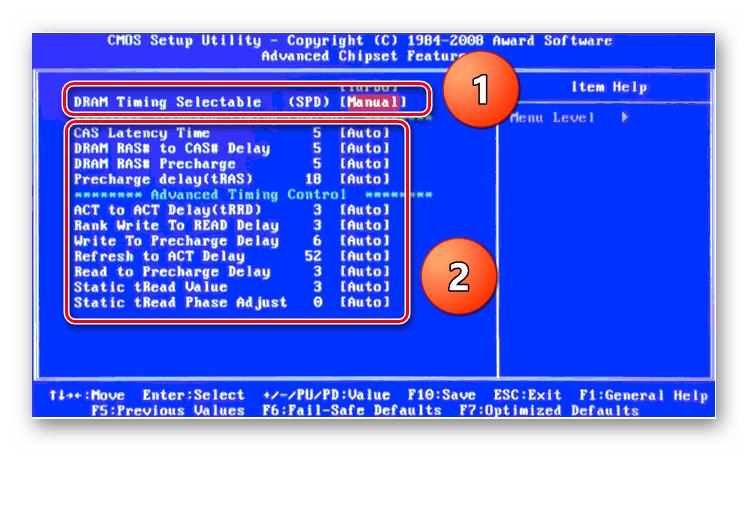
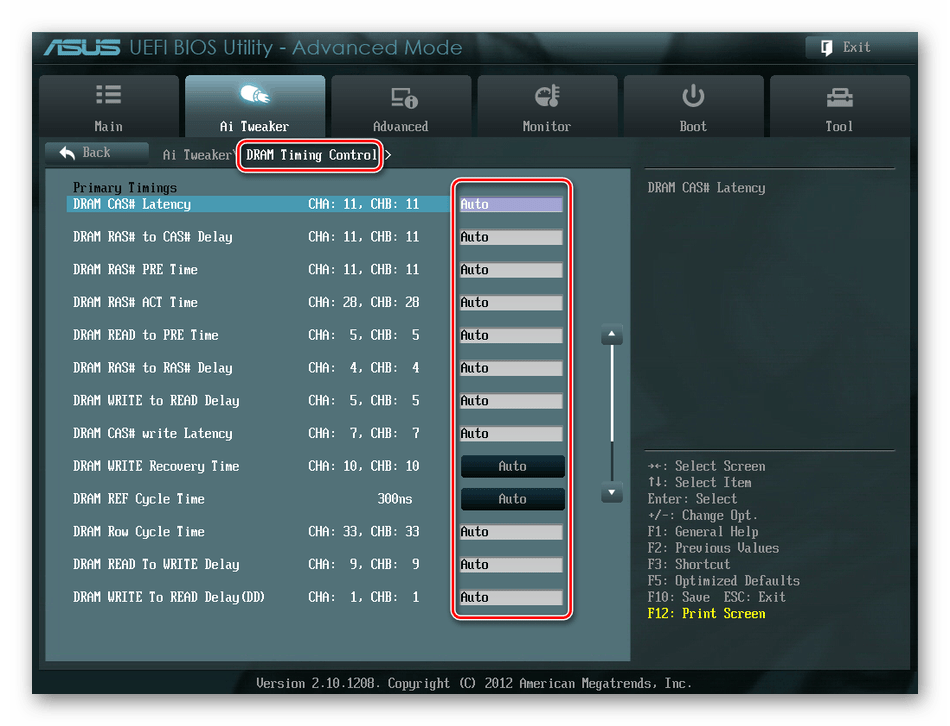
Продвигаясь ниже по меню, видим строку «DRAM Timing Control» и нажав на нее, попадаем в раздел регулировки различных таймингов RAM. ПО умолчанию во всех полях стоит «Auto», но при желании можно попробовать поставить свои значения времени отклика.
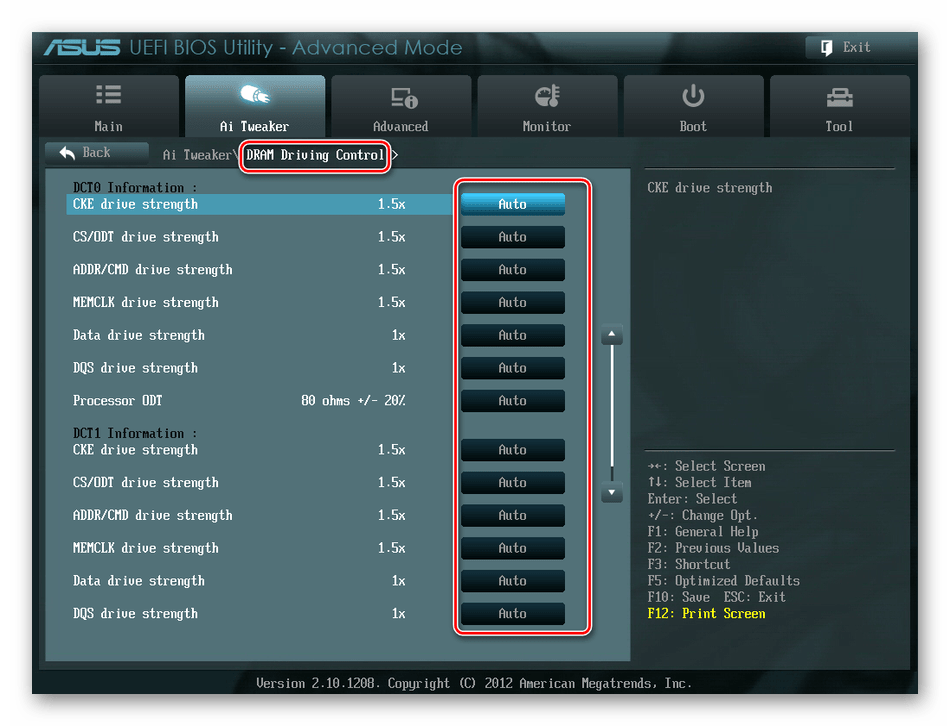
Возвращаемся в меню «Ai Tweaker» и заходим в «DRAM Driving Control». Здесь можно попытаться чуть увеличить множители частоты RAM и ускорить её работу. Но делать это надо осознанно и осторожно.
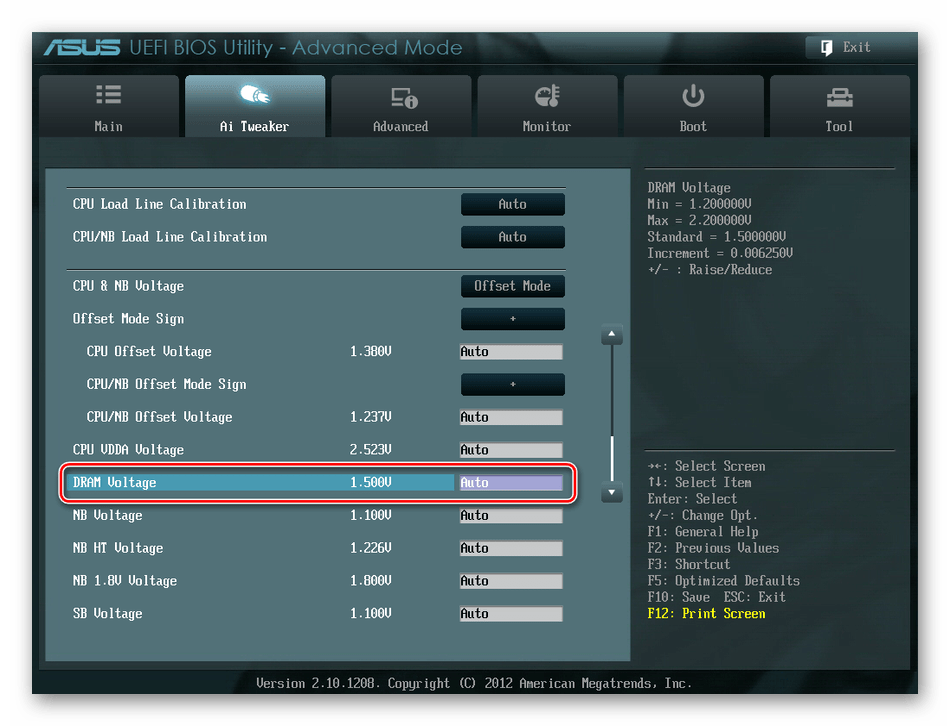
Опять возвращаемся на прошлую вкладку и далее наблюдаем параметр «DRAM Voltage», где можно изменять подаваемое на модули оперативной памяти напряжение электрического тока. Повышать вольтаж можно на минимальные значения и поэтапно.
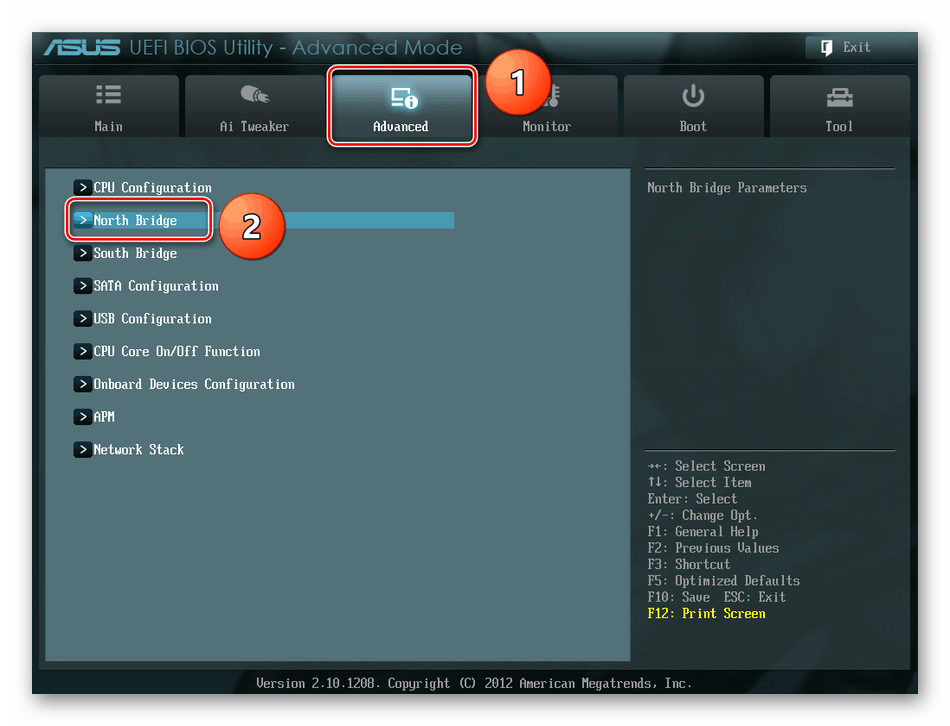
Затем выходим в окно расширенных настроек и передвигаемся во вкладку «Advanced». Там посещаем «North Bridge», страницу северного моста материнской платы.
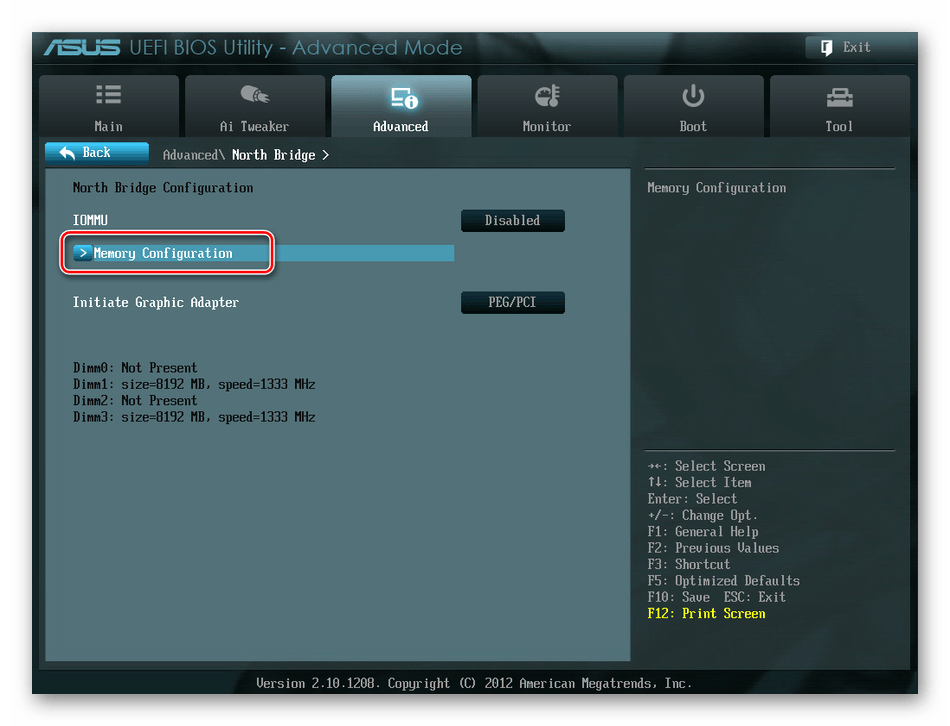
Здесь нас интересует строка «Memory Configuration», на которую и нажимаем.
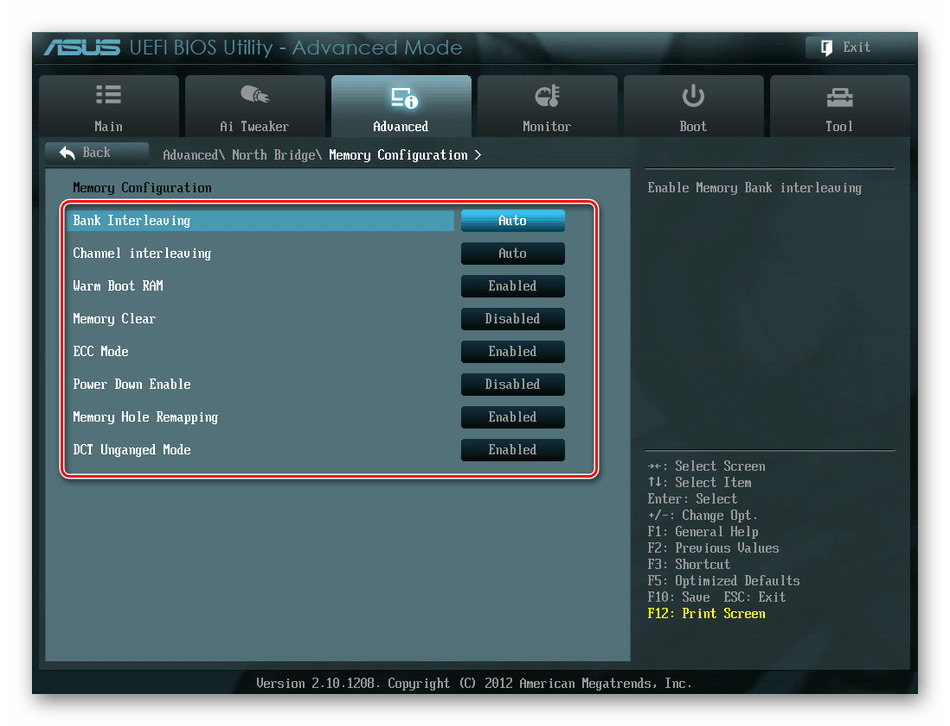
В следующем окне можно изменить параметры конфигурации модулей оперативной памяти, установленных в ПК. Например, включить или выключить контроль и коррекцию ошибок (ECC) RAM, определить режим чередования банков оперативной памяти и так далее.
Как вы увидели, настройка оперативной памяти в БИОС вполне возможна для опытного пользователя. В принципе, в случае ваших некорректных действий на этом направлении компьютер просто не включится или прошивка сама сбросит ошибочные значения. Но осторожность и чувство меры не помешает. И помните, что износ модулей RAM при увеличенных показателях соответственно ускоряется.
Отблагодарите автора, поделитесь статьей в социальных сетях.
The BIOS for this motherboard is standard for server motherboards, so we will only show a few BIOS screens.
This is the main BIOS screen, which shows basic system information.
The Advanced tab brings you to the main advanced screen.
This is the Advanced Boot Feature menu.
Use this feature to select the screen display between POST messages, or the OEM logo at bootup. Select Disabled to display the POST messages. Select Enabled to display the OEM logo instead of the normal POST messages.
Add-On ROM Display Mode:
Use this item to set the display mode for the Option ROM.
INT19 (Interrupt 19) Trap Response:
Interrupt 19 is the software interrupt that handles the boot disk function.
Watch Dog Function:
Select Enabled to allow the Watch Dog timer to reboot the system when it is inactive for more than five minutes.
This is the CPU Configuration screen.
Clock Spread Spectrum:
Select Enabled to allow the BIOS to monitor and attempt to reduce the level of electromagnetic interference caused by the components.
This feature allows you to determine the number of CPU cores to enable. Enter «0» to enable all cores.
Select Unlock/Enable to use the Protected-Processor Inventory Number (PPIN) control in the system.
The Hardware Prefetcher will prefetch streams of data and instructions from the main memory to the L2 cache to improve CPU performance.
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch:
Select Enable for the CPU to prefetch both cache lines for 128 bytes as comprised.
Select Disable for the CPU to prefetch both cache lines for 64 bytes.
DCU (Data Cache Unit) Streamer Prefetcher:
The DCU Streamer Prefetcher will prefetch data streams from the cache memory to the DCU (Data Cache Unit) to speed up data accessing and processing to enhance CPU performance.
The IP Prefetcher in the DCU (Data Cache Unit) will prefetch IP addresses to improve network connectivity and system performance.
Set the data-prefecting mode for the DCU (Data Cache Unit).
The options are 32KB eight-way without ECC and 16KB four-way with ECC.
Direct Cache Access (DCA):
Intel DCA (Direct Cache Access) technology will improve the efficiency of data transferring and accessing.
DCA Prefetch Delay:
The DCA prefetcher is used with a TOE (TCP/IP Offload Engine) adapter to prefetch data in order to shorten execution cycles and maximize data processing efficiency.
X2 APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller):
Based on Intel’s Hyper-Threading architecture, each logical processor (thread) is assigned 256 APIC IDs (APIDs) in 8-bit bandwidth. When this feature is set to Enable, the APIC ID will expand(X2) from 8-bits to 16-bits to provide 512 APIDs to each thread for CPU performance enhancement.
Intel Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) uses a New Instructions (NI) to ensure data security.
Now we are looking at the Advanced Power Management Configuration screen.
CPU P State Control:
EIST (Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology) allows the system to automatically adjust the processor voltage and core frequency to reduce power consumption and heat dissipation.
This feature is used to change the P-state (Power-Performance State) coordination type. P-state is also known as «SpeedStep» for Intel processors.
CPU C State Control:
Use this to set the limit on the C-State package register.
Select Enable to allow the BIOS to report the CPU C3 State (ACPI C2) to the operating system. During the CPU C3 State, the CPU clock generator is turned off.
Enhanced Halt State (C1E):
Select Enabled to use Enhanced Halt-State technology, which will significantly reduce CPU power consumption by reducing CPU clock cycles and voltages during a halt-state.
CPU T State Control:
ACPI (Advanced Configuration Power Interface) T-States supports CPU throttling by the operating system to reduce power consumption.
This is the QPI Configuration screen.
The main feature to look at here is CoD (Cluster-on-Die), which enhances system performance in cloud computing.
CoD reduces coherence traffic and cache-to-cache transfer latencies, and targets NUMA (non-uniform memory access) optimized workloads where latency is more important than sharing caching agents. CoD is best used for highly NUMA (non-uniform memory access) optimized workloads.
Each Home agent has
14KB of cache, which is eight-way, 256 sets, and two-sector wide. It stores 8-bit presence vector tracking caching agent, potentially owning a copy a cache line; allocation on a cache-to-cache transfer, and tracks hit-M, hit-E, and hit-S lines, which are hotly contested cache lines.
The result is lower cache-to-cache transfer latencies, and reduced directory updates and reads of hotly contested lines. Snoop traffic is also reduced by sending directed snoops, rather than broadcasting them.
Now we are looking at the Integrated Memory Controller (IMC) screen:
Enforce POR restrictions on DDR4 frequency and voltage programming.
Enable data scrambling to enhance system performance and data integrity.
ADR (Automatic Diagnostic Repository) support enhances memory performance.
DRAM RAPL (Running Average Power Limit) Baseline:
Set the runtime power-limit baseline for DRAM modules.
Set Throttling Mode (Closed Loop Thermal Throttling):
Throttling improves CPU reliability, and reduces power consumption via automatic-voltage control during CPU idle states.
Set the A7 (Addressing) mode to improve memory performance.
Next up is the IIO Configuration settings.
EV DFX (Device Function On-Hide) Features:
The EV_DFX Lock Bits that are located on a processor will always remain clear during electric tuning.
IOU2 (II0 PCIe Port 1):
This configures the PCI-E port Bifurcation setting for a PCI-E port.
II01 PORT 1A Link Speed:
This feature configures the link speed of a PCI-E port specified by the user, Gen 1, Gen 2, Gen 3.
IOAT (Intel IO Acceleration) Configuration:
Intel I/OAT (I/O Acceleration Technology) support significantly reduces CPU overhead by leveraging CPU architectural improvements, and freeing the system resource for other tasks.
Intel VT for Directed I/O (VT-d):
The Intel Virtualization Technology provides support for Direct I/O VT-d, by reporting the I/O device assignments to the VMM (Virtual Machine Monitor) through the DMAR ACPI tables. This feature offers fully protected I/O resource sharing across Intel platforms, providing greater reliability, security, and availability in networking and data sharing.
Now we are looking at the USB Configuration screen.
This is the PCIe/PCI/PnP Configuration screen.
SR-IOV is available if the system supports Single-Root Virtualization.
With this option, the Active State Power Management (ASPM) level for PCI-E devices with auto set in the system BIOS will automatically set the ASPM level based on the system configuration.
This is the ACPI Settings screen.
Select Enabled to support the Windows Hardware Error Architecture (WHEA) platform, and provide a common infrastructure for the system to handle hardware errors within the Windows OS environment to reduce system crashes, and to enhance system recovery and health monitoring.
NUMA (Available when the OS supports this feature):
Non-Uniform Memory Access support enhances system performance.
The last screen we will look at is the Boot Configuration screen. Here you can see all of the boot options available for the system.
Remote Management
The IPMI 2.0 with virtual media supplies remote access over LAN and KVM, over LAN support. Be sure to have a LAN cable plugged into the Dedicated IPMI LAN port.
We find our remote access IP address located in the BIOS under the IPMI Tab. In our case, this was 192.182.1.36. Enter yours into your browser, and you will see the login screen.
As a best practice, administrative users should change factory default login information before connecting any new server to their network.
After logging in, we come to the home screen and see system information displayed.
There is also a remote control option for iKVM.
The next tab is the Sensor Readings menu.
The Configuration menu allows you to change many features on the server, Active Directory settings, DNS, LDAP, and many more.
The power control and status menu allows you to power on, shut down, restart, and cycle the server.
The Virtual Media menu allows you to mount or share virtual media like Floppy Disks and CD-ROM images.
The Maintenance menu allows you to update the firmware, and restore factory defaults.
The Miscellaneous menu allows post snooping, SMC RAKP enable/disable, UID control, and BIOS recovery.
PRICING: You can find products similar to this one for sale below.