Что такое undo oracle
10 Managing the Undo Tablespace
This chapter describes how to manage the undo tablespace, which stores information used to roll back changes to the Oracle Database. It contains the following topics:
Part III, «Automated File and Storage Management» for information about creating an undo tablespace whose datafiles are both created and managed by the Oracle Database server.
Undo records are used to:
Roll back transactions when a ROLLBACK statement is issued
Recover the database
Provide read consistency
Analyze data as of an earlier point in time by using Oracle Flashback Query
Recover from logical corruptions using Oracle Flashback features
When a ROLLBACK statement is issued, undo records are used to undo changes that were made to the database by the uncommitted transaction. During database recovery, undo records are used to undo any uncommitted changes applied from the redo log to the datafiles. Undo records provide read consistency by maintaining the before image of the data for users who are accessing the data at the same time that another user is changing it.
Introduction to Automatic Undo Management
This section introduces the concepts of Automatic Undo Management and discusses the following topics:
Overview of Automatic Undo Management
You set the UNDO_MANAGEMENT initialization parameter to AUTO to enable automatic undo management. A default undo tablespace is then created at database creation. An undo tablespace can also be created explicitly. The methods of creating an undo tablespace are explained in «Creating an Undo Tablespace».
When the instance starts, the database automatically selects the first available undo tablespace. If no undo tablespace is available, then the instance starts without an undo tablespace and stores undo records in the SYSTEM tablespace. This is not recommended in normal circumstances, and an alert message is written to the alert log file to warn that the system is running without an undo tablespace.
If the database contains multiple undo tablespaces, you can optionally specify at startup that you want to use a specific undo tablespace. This is done by setting the UNDO_TABLESPACE initialization parameter, as shown in this example:
In this case, if you have not already created the undo tablespace (in this example, undotbs_01 ), the STARTUP command fails. The UNDO_TABLESPACE parameter can be used to assign a specific undo tablespace to an instance in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment.
The following is a summary of the initialization parameters for automatic undo management:
When automatic undo management is enabled, if the initialization parameter file contains parameters relating to manual undo management, they are ignored.
Oracle Database Reference for complete descriptions of initialization parameters used in automatic undo management
Undo Re tention
After a transaction is committed, undo data is no longer needed for rollback or transaction recovery purposes. However, for consistent read purposes, long-running queries may require this old undo information for producing older images of data blocks. Furthermore, the success of several Oracle Flashback features can also depend upon the availability of older undo information. For these reasons, it is desirable to retain the old undo information for as long as possible.
Oracle Database automatically tunes the undo retention period based on undo tablespace size and system activity. You can specify a minimum undo retention period (in seconds) by setting the UNDO_RETENTION initialization parameter. The database makes its best effort to honor the specified minimum undo retention period, provided that the undo tablespace has space available for new transactions. When available space for new transactions becomes short, the database begins to overwrite expired undo. If the undo tablespace has no space for new transactions after all expired undo is overwritten, the database may begin overwriting unexpired undo information. If any of this overwritten undo information is required for consistent read in a current long-running query, the query could fail with the snapshot too old er ror message.
The following points explain the exact impact of the UNDO_RETENTION parameter on undo retention:
The UNDO_RETENTION parameter is ignored for a fixed size undo tablespace. The database may overwrite unexpired undo information when tablespace space becomes low.
Reten tion Guarantee
To guarantee the success of long-running queries or Oracle Flashback operations, you can enable retention guarantee. If retention guarantee is enabled, the specified minimum undo retention is guaranteed; the database never overwrites unexpired undo data even if it means that transactions fail due to lack of space in the undo tablespace. If retention guarantee is not enabled, the database can overwrite unexpired undo when space is low, thus lowering the undo retention for the system. This option is disabled by default.
Enabling retention guarantee can cause multiple DML operations to fail. Use with caution.
You enable retention guarantee by specifying the RETENTION GUARANTEE clause for the undo tablespace when you create it with either the CREATE DATABASE or CREATE UNDO TABLESPACE statement. Or, you can later specify this clause in an ALTER TABLESPACE statement. You disable retention guarantee with the RETENTION NOGUARANTEE clause.
Automatic Tun ing of Undo Retention
Oracle Database automatically tunes the undo retention period based on how the undo tablespace is configured.
If the undo tablespace is fixed size, the database tunes the retention period for the best possible undo retention for that tablespace size and the current system load. This tuned retention period can be significantly greater than the specified minimum retention period.
If the undo tablespace is configured with the AUTOEXTEND option, the database tunes the undo retention period to be somewhat longer than the longest-running query on the system at that time. Again, this tuned retention period can be greater than the specified minimum retention period.
You can determine the current retention period by querying the TUNED_UNDORETENTION column of the V$UNDOSTAT view. This view contains one row for each 10-minute statistics collection interval over the last 4 days. (Beyond 4 days, the data is available in the DBA_HIST_UNDOSTAT view.) TUNED_UNDORETENTION is given in seconds.
Undo Retention Tuning and Alert Thresholds For a fixed size undo tablespace, the database calculates the maximum undo retention period based on database statistics and on the size of the undo tablespace. For optimal undo management, rather than tuning based on 100% of the tablespace size, the database tunes the undo retention period based on 85% of the tablespace size, or on the warning alert threshold percentage for space used, whichever is lower. (The warning alert threshold defaults to 85%, but can be changed.) Therefore, if you set the warning alert threshold of the undo tablespace below 85%, this may reduce the tuned length of the undo retention period. For more information on tablespace alert thresholds, see «Managing Tablespace Alerts».
Setting the Undo Rete ntion Period
To set the undo retention period :
Do one of the following:
Set UNDO_RETENTION in the initialization parameter file.
Change UNDO_RETENTION at any time using the ALTER SYSTEM statement:
The effect of an UNDO_RETENTION parameter change is immediate, but it can only be honored if the current undo tablespace has enough space.
Sizing the Undo Tablespace
You can size the undo tablespace appropriately either by using automatic extension of the undo tablespace or by using the Undo Advisor for a fixed sized tablespace.
Using Auto-Extensible Tablespaces
Oracle Database supports automatic extension of the undo tablespace to facilitate capacity planning of the undo tablespace in the production environment. When the system is first running in the production environment, you may be unsure of the space requirements of the undo tablespace. In this case, you can enable automatic extension of the undo tablespace so that it automatically increases in size when more space is needed. You do so by including the AUTOEXTEND keyword when you create the undo tablespace.
Sizing Fixed-Size Undo Tablespaces
The Undo Advisor relies for its analysis on data collected in the Automatic Workload Repository (AWR). It is therefore important that the AWR have adequate workload statistics available so that the Undo Advisor can make accurate recommendations. For newly created databases, adequate statistics may not be available immediately. In such cases, an auto-extensible undo tablespace can be used.
An adjustment to the collection interval and retention period for AWR statistics can affect the precision and the type of recommendations that the advisor produces. See «Automatic Workload Repository» for more information.
To use the Undo Advisor, you first estimate these two values:
The length of your expected longest running query
After the database has been up for a while, you can view the Longest Running Query field on the Undo Management page of Enterprise Manager.
The longest interval that you will require for flashback operations
For example, if you expect to run Flashback Queries for up to 48 hours in the past, your flashback requirement is 48 hours.
You then take the maximum of these two undo retention values and use that value to look up the required undo tablespace size on the Undo Advisor graph.
The Undo Advisor PL/SQL Interface
After you have created the advisor task, you can view the output and recommendations in the Automatic Database Diagnostic Monitor in Enterprise Manager. This information is also available in the DBA_ADVISOR_* data dictionary views.
Oracle Database 2 Day DBA for more information on using advisors and «Using the Segment Advisor» for an example of creating an advisor task for a different advisor
Oracle Database Reference for information about the DBA_ADVISOR_* data dictionary views
Managing Undo Tablespaces
This section describes the various steps involved in undo tablespace management and contains the following sections:
Управление Undo
Управление Undo
Главным достоинством сегментов undo является то что они управляются автоматически, но вы должны установить ограничения в границах которых Oracle будет осуществлять управление. После того как вы рассмотрели объем данных и активность вашей БД вам нужно установить некоторые параметры и определить размеры табличных пространтсв undo.
Ошибки связанные с undo
Принципы очень просты: во первых, всегда должно быть достаточно места для undo чтобы все транзакции могли работать и, во вторых, всегда должно быть достаточно данных undo чтобы запросы выполнились успешно. Первый принцип требует чтобы табличное пространство undo было достаточно большим чтобы накапливать undo данные для худшего сценария. Должно быть выделено достаточно места для хранения данных во время пиковой нагрузки. Обратите внимание что это не значит в момент максимального количества конкурирующих транзакций; во время обычной работы у вас может быть много транзакций, но суммарное количество данных undo которые они сгенерируют будет гораздо меньше чем сгенерирует одна долгая транзакция запускаемая в конце месяца. Второй принцип требует наличие в табличном пространстве места для хранения неустаревших данных которые могут требоваться для согласованности чтения.
Если транзакции недостаточно места, последний запрос выполнится с ошибкой ORA-30036 “unable to extend segment in undo tablespace”. Запрос будет отменён, но все остальные запросы внутри транзакции останутся выполненными и неподтверждёнными. Алгоритм которы выделяет место для undo сегментов внутри табличного пространтсва undo вызовет такую ошибку только если табличное пространтсво полностью состоит из активных данных.
Если DML запрос выполняется с ошибкой выделения места, он будет отменен. Остальные запросы транзакции которые уже выполнены успешно остаются без изменений и неподтверждены.
Если запрос обнаруживает что блок данных нужный для запроса был изменен после начала выполнения запроса, серверный процесс возьмёт «старые» данные из сегмента undo. Если в undo сегменте этот блок был переписан, запрос вернёт ошибку ORA-1555 ”snapshot too old”.
Если табличное пространство undo недостаточно велико – у Oracle есть выбор: позволить транзакции переписать неустаревшие данные и позволить запросу SELECT не выполнится успешно, или позволить запросу SELECT выполнится успешно, а транзакции вернуть ошибку. По умолчанию транзакции имеют больший приоритет: Oracle перезапишет неустаревшие undo.
Параметры для управления undo и гарантия удержания данных (retention guarantee)
Доступно три параметра для управления undo: UNDO_MANAGEMENT, UNDO_TABLESPACE и UNDO_RETENTION.
У параметра UNDO_MANAGEMENT значения по умолчанию AUTO начиная с версии 11g. Возможно установить это значение в MANUAL, и это приведёт к тому что Oracle не будет использовать сегменты undo. Это позволено для обратной совместимости, и если вы решите использовать это, вам придётся тратить много времени на управление и тюнинг сегментов rollback. Лучше не делайте это. Oracle настоятельно рекомендует использовать значение AUTO и разрешить использование сгементов undo. Этот параметр статический, т.е. если вы измените значение вам нужно перезапустить экземпляр БД. Остальные параметры динамический – их можно изменять во время работы экземпляра.
Если вы используете UNDO_MANAGEMENT=AUTO то вы должны указать UNDO_TABLESPACE. Этот параметр указывает активное табличное пространство, которое должно было быть создано как UNDO TABLESPACE. Все сегменты undo будут создаваться и переводиться в режим online автоматически.
И наконец параметр UNDO_RETENTION, который устанавливается в секундах, не обязательный к выполнению. Этот параметр указывает как долго хранить неактивные undo данные перед тем как обозначить их как устаревшие. Если например самый долгий запрос выполняется тридцать минут, вы можете установить этот параметр в 1800. Oracle постарается хранить все undo данные как минимум 30 минут, и ваш запрос должен всегда выполниться успешно, а не вернуть ошибку ORA-1555. Если вы не установили этот параметр, или установили значение 0, Oracle всё равно будет хранить undo данные так долго, как только возможно. Алгоритм который определяет какие данные устарели всегда будет переписывать самые старые данные; таким образом UNDO_RETENTION всегда имеет максимально допустимое значение от размера табличного пространства.
Можно настроить параметр UNDO_RETENTION как обязательный, и undo данные всегда будут храниться столько сколько указано. По умолчанию Oracle выставляет приоритет для транзакций, а не запросов. Если размера не хватает на хранение старых данных для запросов или записи новых для транзакций, Oracle отдаст предпочтение транзакции и перезапишет неактивное undo чтобы транзакция работала без ошибки ORA-30036. Другими словами сохранение undo это лишь необязательная задача которую Oracle пытается по возможности выполнять. Однако иногда бывает ситуация когда успешное выполнение запроса важнее чем транзакции. Например запрос на закрытие месяца, когда нужно выполнить долгий запрос, а транзакции могут подождать пару часов, пока отчёт выполняется. Или если вам нужны flashback запросы, которые работают с undo данными.
Гарантированное удержание данных (guaranteed undo retention), что означает что данные никогда не будут переписаны пока не пройдёт время указанное в UNDO_RETENTION, включается для табличного пространства. Это свойство можно указать во время создания табличного пространтсва или изменить позже. Когда вы активируете табличное пространтсво для которого указано retention guarantee, все запросы будут выполнены успешно если они выполняются быстрее чем значение UNDO_RETENTION; вы никогда не больше не встретите ошибку “snapshot too old”. Обратной стороной медали будет то что транзакции могут не выполниться из-за нехватки места.
Если параметр UNDO_RETENTION был установлен и файлы данных табличного пространтсва undo используют режим autoextend, то Oracle автоматически будет увеличивать размер файлов данных для хранения undo данных минимум время указанное в UNDO_RETENTION. Таким образом комбинирование autoextending файлов данных и гарантированного хранения undo данных позволяет выполнять успешно и транзакции и запросы – конечно если у вас достаточно дискового пространтсва. Если у вас недостаточно места – попытка увеличить размер файла будет неуспешной.
У БД может быть одно табличное пространство используемое в обычной работе, где retention guarantee не настроек, и второе для долгих запросов где хранение данных гарантированно.
Оценка размера и мониторинг табличного пространтсва undo
Табличное пространтсво должно быть достаточно большим чтобы хранить undo данные параллельных транзакций в пиковый момент нагрузки, плюс достаточно неустаревших данных для успешного выполнения самого долгого запроса. Также вам возможно придётся добавить места для flashback запросов. Алгоритм прост: расчитать скорость генерации undo при максимальной нагрузке и умножить на длительность самого долгого запроса.
Представление V$UNDOSTAT расскажет вам то что вам надо знать. Так же доступен помошник в Database Control, который покажет информацию в максимально понятной форме.
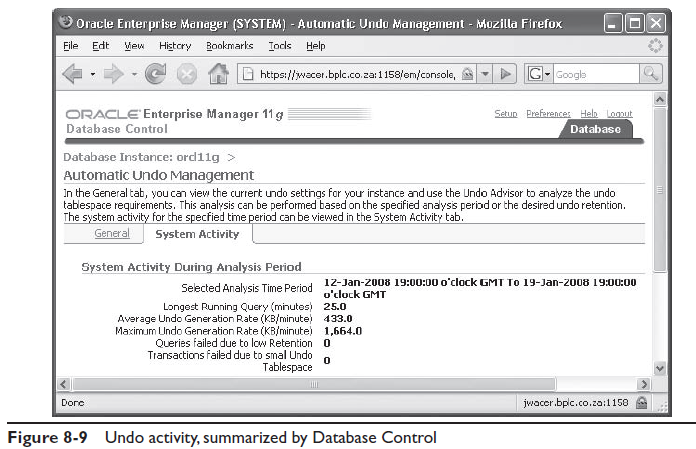
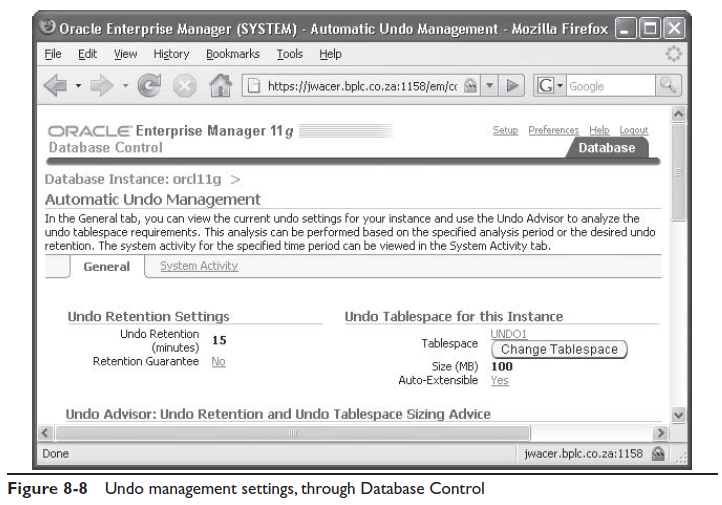
На рисунке 8-8 показан экран управления undo в Database Control. Из домашней страницы перейдите на вкладку Server и затем перейдите по ссылке Automatic Undo Management в разделе Database Configuration.
На рисунке примера мы видим что табличное пространтсво называется UNDO1 и размер 100 Мб. Хранение undo не гарантировано но файлы данных табличного пространство авторасширяемы. Если вы выбрали авто-расширение для файлов, это гарантирует вам что ваши транзакции всегда выполнятся (пока у вас есть место), но Oracle не будет увеличивать их размер для выполнения UNDO_RETENTION; запрос может вернуть ошибку “snapshot too old”. Как-бы то ни-было, вы не должны рассчитывать на auto-extend; ваше табличное пространство должно быть настроено что быть достаточно большим. Кнопка Change tablespace вызовет команду ALTER SYSTEM для изменения активного табличного пространтсва.
Дополнительная информация на вкладке System Activity, показанная на рисунке 8-9, рассказывает вам что пиковая геренация undo всегд 1664Кб в минуту, и самый долгий запрос был 25 минут. Отсюда следует что минимальный размер табличного пространтсва undo будет 1664*25=40265 Кб, что всего лишь 40 Мб. Елси текущий размер меньше, это оторазится в секции помошника Undo. Пока что не было ошибок транзакций, и ошибок запросов вызванных недостатком места или перезаписью данных undo.
Создание и управление табличных пространтсв undo
С точки зрения управления файлами, табличное пространство undo такое же как другие табличные пространтсва: файлы можно добавлять, изменять размер, включать, выключать, перемещать и переименовывать. Но вы не можете указать свойства хранения: не можете указать метод управления пространтсвом сегментов, или uniform extent size. Для создания табличного пространства undo используется ключевое слово UNDO
CREATE UNDO TABLESPACE tablespace_name
DATAFILE datafile_name SIZE size
[ RETENTION NOGUARANTEE | GUARANTEE ] ;
По умолчанию табличное пространство создаётся RETENTION NOGUARANTEE. Это можно или указать явно при создании, либо изменить позднее выполнив
ALTER TABLESPACE tablespace_name retention [ GUARANTEE | NOGUARANTEE ] ;
Пока вы не укажете явно при создании, файлы данных табличного пространтсва undo не будут авто-расширяемы. Но если вы создавали базу данных используя DBCA, то будет включено авто-расширение файлов и максимальный размер файлов будет неограничен. Автоматическое расширение может быть включено или отключено в любое время, как для любого файла данных.
Невозможно создать сегменты в табличном пространстве undo, кроме тех сегментов undo которые будут созданы автоматически. Вначале будет группа из десяти сегментов undo которые создаются при создании табличного пространтсва. Затем буду т создаваться дополнительные сегменты если в базе будет больше чем десять параллельных транзакций. Oracle следит за количество параллельных транзакций и создаёт сегменты при необходимости.
Неважно сколько у вас табличных пространств undo в базе данных, грубо говоря, только одна будет использоваться в определённый момент. Сегменты undo в актвном табличном пространстве имеют статус online (т.е. доступны для использования); а сегменты в других табличных пространствах будут иметь статус offline, т.е. то что они не могут использоваться. Если табличное пространтсво undo изменяется, все сегменты в старом табличном пространтсве будут выключаться, а сегменты нового табличного пространтсва будут включены. Но бывает два исключения, это
RAC база данных. В каждом экземпляре БД должно быть своё табличное пространтсво undo. Это можно контролировать установив разное значение параметра UNDO_TABLESPACE для каждого экземпляра. Каждый экземпляр управляет статусом своих сегментов undo
Если табличное пространтсво undo изменяется путём указания нового значения UNDO_TABLESPACE, то любые сегменты в предыдущем табличном пространстве связанные с активной транзакцией будут online пока транзакция не закончит работу.
16 Managing Undo
Chapter 17, «Using Oracle Managed Files»for information about creating an undo tablespace whose data files are both created and managed by Oracle Database.
Undo records are used to:
Roll back transactions when a ROLLBACK statement is issued
Recover the database
Provide read consistency
Analyze data as of an earlier point in time by using Oracle Flashback Query
Recover from logical corruptions using Oracle Flashback features
When a ROLLBACK statement is issued, undo records are used to undo changes that were made to the database by the uncommitted transaction. During database recovery, undo records are used to undo any uncommitted changes applied from the redo log to the data files. Undo records provide read consistency by maintaining the before image of the data for users who are accessing the data at the same time that another user is changing it.
Introduction to Automatic Undo Management
This section introduces the concepts of Automatic Undo Management and discusses the following topics:
Overview of Automatic Undo Management
An undo tablespace can also be created explicitly. The methods of creating an undo tablespace are explained in «Creating an Undo Tablespace».
When the instance starts, the database automatically selects the first available undo tablespace. If no undo tablespace is available, the instance starts without an undo tablespace and stores undo records in the SYSTEM tablespace. This is not recommended, and an alert message is written to the alert log file to warn that the system is running without an undo tablespace.
If the database contains multiple undo tablespaces, you can optionally specify at startup that you want to use a specific undo tablespace. This is done by setting the UNDO_TABLESPACE initialization parameter, as shown in this example:
If the tablespace specified in the initialization parameter does not exist, the STARTUP command fails. The UNDO_TABLESPACE parameter can be used to assign a specific undo tablespace to an instance in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment.
Space management for rollback segments is complex. Oracle strongly recommends leaving the database in automatic undo management mode.
The following is a summary of the initialization parameters for undo management:
When automatic undo management is enabled, if the initialization parameter file contains parameters relating to manual undo management, they are ignored.
A null UNDO_MANAGEMENT initialization parameter defaults to automatic undo management mode in Release 11 g and later, but defaults to manual undo management mode in earlier releases. You must therefore use caution when upgrading a previous release to Release 11g. Oracle Database Upgrade Guide describes the correct method of migrating to automatic undo management mode, including information on how to size the undo tablespace.
Oracle Database Reference for complete descriptions of initialization parameters used in undo management
About the Undo Re tention Period
After a transaction is committed, undo data is no longer needed for rollback or transaction recovery purposes. However, for consistent read purposes, long-running queries may require this old undo information for producing older images of data blocks. Furthermore, the success of several Oracle Flashback features can also depend upon the availability of older undo information. For these reasons, it is desirable to retain the old undo information for as long as possible.
Oracle Database automatically tunes the undo retention period based on undo tablespace size and system activity. You can optionally specify a minimum undo retention period (in seconds) by setting the UNDO_RETENTION initialization parameter. The exact impact this parameter on undo retention is as follows:
The UNDO_RETENTION parameter is ignored for a fixed size undo tablespace. The database always tunes the undo retention period for the best possible retention, based on system activity and undo tablespace size. See «Automatic Tuning of Undo Retention» for more information.
Automatic Tun ing of Undo Retention
Oracle Database automatically tunes the undo retention period based on how the undo tablespace is configured.
If the undo tablespace is configured with the AUTOEXTEND option, the database dynamically tunes the undo retention period to be somewhat longer than the longest-running active query on the system. However, this retention period may be insufficient to accommodate Oracle Flashback operations. Oracle Flashback operations resulting in snapshot too old errors are the indicator that you must intervene to ensure that sufficient undo data is retained to support these operations. To better accommodate Oracle Flashback features, you can either set the UNDO_RETENTION parameter to a value equal to the longest expected Oracle Flashback operation, or you can change the undo tablespace to fixed size.
If the undo tablespace is fixed size, the database dynamically tunes the undo retention period for the best possible retention for that tablespace size and the current system load. This best possible retention time is typically significantly greater than the duration of the longest-running active query.
If you decide to change the undo tablespace to fixed-size, you must choose a tablespace size that is sufficiently large. If you choose an undo tablespace size that is too small, the following two errors could occur:
DML could fail because there is not enough space to accommodate undo for new transactions.
Long-running queries could fail with a snapshot too old error, which means that there was insufficient undo data for read consistency.
Reten tion Guarantee
To guarantee the success of long-running queries or Oracle Flashback operations, you can enable retention guarantee. If retention guarantee is enabled, the specified minimum undo retention is guaranteed; the database never overwrites unexpired undo data even if it means that transactions fail due to lack of space in the undo tablespace. If retention guarantee is not enabled, the database can overwrite unexpired undo when space is low, thus lowering the undo retention for the system. This option is disabled by default.
Enabling retention guarantee can cause multiple DML operations to fail. Use with caution.
You enable retention guarantee by specifying the RETENTION GUARANTEE clause for the undo tablespace when you create it with either the CREATE DATABASE or CREATE UNDO TABLESPACE statement. Or, you can later specify this clause in an ALTER TABLESPACE statement. You disable retention guarantee with the RETENTION NOGUARANTEE clause.
Undo Retention Tuning and Alert Thresholds
For a fixed-size undo tablespace, the database calculates the best possible retention based on database statistics and on the size of the undo tablespace. For optimal undo management, rather than tuning based on 100% of the tablespace size, the database tunes the undo retention period based on 85% of the tablespace size, or on the warning alert threshold percentage for space used, whichever is lower. (The warning alert threshold defaults to 85%, but can be changed.) Therefore, if you set the warning alert threshold of the undo tablespace below 85%, this may reduce the tuned size of the undo retention period. For more information on tablespace alert thresholds, see «Managing Tablespace Alerts».
Tracking the Tuned Undo Retention Period
You can determine the current retention period by querying the TUNED_UNDORETENTION column of the V$UNDOSTAT view. This view contains one row for each 10-minute statistics collection interval over the last 4 days. (Beyond 4 days, the data is available in the DBA_HIST_UNDOSTAT view.) TUNED_UNDORETENTION is given in seconds.
Setting the Minimum Undo Rete ntion Period
To set the minimum undo retention period :
Do one of the following:
Set UNDO_RETENTION in the initialization parameter file.
Change UNDO_RETENTION at any time using the ALTER SYSTEM statement:
The effect of an UNDO_RETENTION parameter change is immediate, but it can only be honored if the current undo tablespace has enough space.
Sizing a Fixed-Size Undo Tablespace
The Undo Advisor relies for its analysis on data collected in the Automatic Workload Repository (AWR). It is therefore important that the AWR have adequate workload statistics available so that the Undo Advisor can make accurate recommendations. For newly created databases, adequate statistics may not be available immediately. In such cases, continue to use the default auto-extending undo tablespace until at least one workload cycle completes.
An adjustment to the collection interval and retention period for AWR statistics can affect the precision and the type of recommendations that the advisor produces. See Oracle Database Performance Tuning Guide for more information.
To use the Undo Advisor, you first estimate these two values:
The length of your expected longest running query
After the database has completed a workload cycle, you can view the Longest Running Query field on the System Activity subpage of the Automatic Undo Management page.
The longest interval that you will require for Oracle Flashback operations
For example, if you expect to run Oracle Flashback queries for up to 48 hours in the past, your Oracle Flashback requirement is 48 hours.
You then take the maximum of these two values and use that value as input to the Undo Advisor.
Running the Undo Advisor does not alter the size of the undo tablespace. The advisor just returns a recommendation. You must use ALTER DATABASE statements to change the tablespace data files to fixed sizes.
To make the undo tablespace fixed-size, Oracle suggests that you first allow enough time after database creation to run a full workload, thus allowing the undo tablespace to grow to its minimum required size to handle the workload. Then, you can use the Undo Advisor to determine, if desired, how much larger to set the size of the undo tablespace to allow for long-running queries and Oracle Flashback operations.
Oracle Database 2 Day DBA for instructions for computing the minimum undo tablespace size with the Undo Advisor
The Undo Advisor PL/SQL Interface
«Using the Segment Advisor» for an example of creating an advisor task for a different advisor
Oracle Database Reference for information about the DBA_ADVISOR_* data dictionary views
Managing Undo Tablespaces
This section describes the various steps involved in undo tablespace management and contains the following sections: