Что такое plop boot manager
Использование Plop Boot Manager для загрузки с USB
Plop Boot Manager создан, чтобы преодолеть эти ограничения. Как и прочие менеджеры загрузки, при первом запуске он предлагает меню, где можно выбрать раздел, с которого будет происходить загрузка. Так как он имеет собственные драйверы USB, вы можете использовать его, чтобы заставить старые машины загружаться с флешки. Это очень гибко настраиваемая программа. Например, вы можете задать загрузку GRUB или меню загрузчика Windows, или даже выбрать более экзотические варианты, такие как загрузку Plop с дискеты с последующей инициацией сетевой загрузки. Мы разберем один случай, в котором я использовал Plop, чтобы активировать загрузку с USB на своей старой машине.
Стандартное предупреждение: при выполнении таких задач, как описанная в данной статье, одна ошибка или баг программы может легко уничтожить содержимое целого диска. Сделайте резервную копию важных данных.
В данном случае я устанавливал Plop в MBR, так как это самый простой случай. Здесь необходимо обратить внимание на следующую вещь: если существующая инсталляция GRUB также была записана в MBR, она будет перезаписана. Так как Plop не является загрузчиком Linux, это значит, что Linux перестанет загружаться. Другими словами, вам необходимо переустановить GRUB непосредственно на раздел, в котором у вас установлен Linux. Проблема может заключаться в том, что USB-клавиатуры не будут работать до загрузки операционной системы, поэтому вы не сможете выбрать нужный пункт в меню GRUB, если используете USB-клавиатуру. Естественно, Plop Boot Manager позволяет выбирать загрузку нужной операционной системы. Имеющаяся на компьютере инсталляция Windows продолжит работать без каких-либо дополнительных модификаций.
В архиве имеется несколько директорий с файлами, необходимыми для различных типов инсталляции. Я выбрал ISO-образ инсталлятора (всего 480 кб) и прожег его на CDR. Как я уже говорил, если на вашей машине нет возможности загрузиться с CD, вы можете установить Plop непосредственно из операционной системы, в которой вы работаете. Как и все программы такого рода, инсталлятор представляет из себя смесь текстового и графического режимов. Это простая система и установка занимает очень мало времени.
После перезагрузки вы получите возможность загрузки с различных типов медиа. Как я и надеялся, у меня получилось загрузить Xubuntu с USB-флешки. К стыду разработчиков нужно сказать, что программа не поддерживает загрузку с USB-приводов DVD/CDROM. Это интерактивный менеджер загрузки, поэтому вы можете настраивать его на лету.
Загрузка с USB-флешки при помощи программы Plop boot manager

После установки Plop boot manager и запуска программы появляется меню, где можно выбрать загрузочный раздел. Благодаря тому, что раздел имеет собственные USB-драйвера, возможно произвести загрузку даже с тех устройств, на которых в силу ряда причин не получается или не предусмотрена загрузка через USB интерфейс. Например, распространённой проблемой является загрузка на старом компьютере с USB флеш-накопителя, компьютер просто на просто не видит флешку.
Основные возможности программы
Программа свободно распространяется и абсолютна бесплатна.
Также на сайте можно найти подробные инструкции как пользоваться программой.
Как удалить Plop boot manager
Вот и всё! Программа Plop boot manager успешно удалена. Удачи!
IT_blogs
* CD/DVD boot without BIOS support
* USB boot without BIOS support (UHCI, OHCI and EHCI)
* Floppy boot
* Different profiles for operating systems
* Define up to 16 partitions
* No extra partition for the boot manager
* Hidden boot, maybe you have a rescue system installed and the user should not see that there is another system installed
* Boot countdown
* Hide partitions
* Password protection for the computer and the boot manager setup
* Backup of partition table data
* Textmode user interface 80×50
* Graphic user interface 640×480, 800×600, 1024×786, 1280×1024
* MBR partition table edit
* Start of the boot manager from harddisk, floppy, USB, CD, DVD
* Starting from Windows boot menu
* Starting from LILO, GRUB, Syslinux, Isolinux, Pxelinux (network)
* The boot manager is freeware
Например Ваша мат.плата выдаёт USB 2.0 скорость в ОС Windows или Linux, но при загрузке с USB работает на USB 1.1 и грузиться ОЧЕНЬ медленно.
Начнём Мы как обычно с установки.
Кратко рассмотрим некоторые варианты установки, благо разработчики позаботились о том, что-бы Plop можно было быстро и легко установить практически на любой носитель информации.
Хотите установить Plop на дискету?
Нет ничего проще, просто выполните:
Для ОС Linux:
Хотите установить Plop на CD диск?
Просто прожгите ISO образ на свой носитель.
Установка Plop:
Для ОС DOS:
1) Скачайте plpgenbtldr-0.5.zip
2) Скопируйте файлы plpinstc.com и plpgenbtldr.exe в корень диска C:
3) Переименуйте файл plpinstc.com в plpbt.bin
4) Откройте shell с правами администратора системы
5) Выполните файл plpgenbtldr который создаст файл plpbtldr.bin, это займёт несколько секунд.
Если это займёт больше времени, то значит что-то пошло не так.
Для Windows 2K и XP:
Просто впишите эту строчку в Ваш файл boot.ini:
Разумеется файл plpbtldr.bin должен быть в корне диска c:
Для Windows Vista:
Просто выполните такую команду:
bcdedit /create /d «Install PLoP Boot Manager» /application bootsector
После выполнения этой команды вы получите номер в < >скобках.
Этот номер зовётся (Called) id
Дальше выполните следующие команды, заменяя id на свой, полученный из предыдущей команды:
bcdedit /set
bcdedit /displayorder
* для Syslinux это syslinux.cfg
* для Isolinux это isolinux.cfg
* для Pxelinux это pxelinux.cfg/default
Файл plpinstc положите в корень папки с конфигами.
Если же Вам просто нужно запустить Plop без его установки, то впишите такие строчки:
Файл plpbt так-же положите в корень папки с конфигами и в загрузчике выберите пункт plp
Установка с использование LILO:
Скопируйте файл plpinstc.com в папку /boot
В файл /etc/lilo.conf допишите:
Для запуска Plop без его установки:
Скопируйте файл plpbt.bin в папку /boot
Добавьте такие строчки в файл lilo.conf:
И выполните команду lilo для обновления конфигурации.
Установка с использование GRUB / grub4dos
Скопируйте файл plpinstc.com в папку /boot
В файл menu.lst впишите следующие строки:
title PLoP Boot Manager Install
root (hd0,0)
kernel /boot/plpinstc.com
Для запуска Plop без его установки:
Скопируйте файл plpbt.bin в папку /boot
В файл menu.lst впишите следующие строки:
title PLoP Boot Manager
root (hd0,0)
kernel /boot/plpbt.bin
Конфигурирование Plop:
Настройка производится путём патчинья самого загрузчика Plop с помощью утилиты plpcfgbt
Например, если Вам нужно сделать загрузку с usb устройства и без лишних вопросов, то введите такую строку:
plpcfgbt.exe stm=hidden cnt=on cntval=1 dbt=usb plpbt.bin
Полный список опций можно посмотреть в файле 1README.TXT в директории с программой.
А теперь рассмотрим реально полезный пример использования Plop:
Задача:
1) Получить USB 2.0 или близкую к нему скорость на тех материнских, которые работают с USB 2.0 только в загруженной ОС, а на этапе загрузки выдают USB 1.1
2) Загрузиться в PCI USB 2.0 внешнего конроллера.
Решение:
1) Устанавливаем Plop на ваш носитель информации, я решил воспользоваться свой BootFlash с Grub4DOS в качестве загрузчика.
Общая схема загрузки будет выглядеть так:
Grub4DOS (usb1.1) => Plop => Grub4DOS (usb 2.0)
Сохраняем и пробуем.
Так-же можно сделать загрузку iso образа через RAM:
Скопируем ISO образ в корень диска, в файл menu.lst впишем следующие строки:
Сохраняем и пробуем.
2) В этом случае мы просто устанавливаем Plop на наш HDD,CD-ROM диск или дискету и в качестве устройства выбираем USB
Plop автоматически просканирует все USB порты и загрузить Ваш LiveUSB накопитель.
Думаю для ознакомления пока-что достаточно.
Возможно в будущим я продолжу публиковать информацию по этому замечательному загрузчику.
* CD/DVD boot without BIOS support
* USB boot without BIOS support (UHCI, OHCI and EHCI)
* Floppy boot
* Different profiles for operating systems
* Define up to 16 partitions
* No extra partition for the boot manager
* Hidden boot, maybe you have a rescue system installed and the user should not see that there is another system installed
* Boot countdown
* Hide partitions
* Password protection for the computer and the boot manager setup
* Backup of partition table data
* Textmode user interface 80×50
* Graphic user interface 640×480, 800×600, 1024×786, 1280×1024
* MBR partition table edit
* Start of the boot manager from harddisk, floppy, USB, CD, DVD
* Starting from Windows boot menu
* Starting from LILO, GRUB, Syslinux, Isolinux, Pxelinux (network)
* The boot manager is freeware
Например Ваша мат.плата выдаёт USB 2.0 скорость в ОС Windows или Linux, но при загрузке с USB работает на USB 1.1 и грузиться ОЧЕНЬ медленно.
Начнём Мы как обычно с установки.
Кратко рассмотрим некоторые варианты установки, благо разработчики позаботились о том, что-бы Plop можно было быстро и легко установить практически на любой носитель информации.
Хотите установить Plop на дискету?
Нет ничего проще, просто выполните:
Для ОС Linux:
Хотите установить Plop на CD диск?
Просто прожгите ISO образ на свой носитель.
Установка Plop:
Для ОС DOS:
1) Скачайте plpgenbtldr-0.5.zip
2) Скопируйте файлы plpinstc.com и plpgenbtldr.exe в корень диска C:
3) Переименуйте файл plpinstc.com в plpbt.bin
4) Откройте shell с правами администратора системы
5) Выполните файл plpgenbtldr который создаст файл plpbtldr.bin, это займёт несколько секунд.
Если это займёт больше времени, то значит что-то пошло не так.
Для Windows 2K и XP:
Просто впишите эту строчку в Ваш файл boot.ini:
Разумеется файл plpbtldr.bin должен быть в корне диска c:
Для Windows Vista:
Просто выполните такую команду:
bcdedit /create /d «Install PLoP Boot Manager» /application bootsector
После выполнения этой команды вы получите номер в < >скобках.
Этот номер зовётся (Called) id
Дальше выполните следующие команды, заменяя id на свой, полученный из предыдущей команды:
bcdedit /set
bcdedit /displayorder
* для Syslinux это syslinux.cfg
* для Isolinux это isolinux.cfg
* для Pxelinux это pxelinux.cfg/default
Файл plpinstc положите в корень папки с конфигами.
Если же Вам просто нужно запустить Plop без его установки, то впишите такие строчки:
Файл plpbt так-же положите в корень папки с конфигами и в загрузчике выберите пункт plp
Установка с использование LILO:
Скопируйте файл plpinstc.com в папку /boot
В файл /etc/lilo.conf допишите:
Для запуска Plop без его установки:
Скопируйте файл plpbt.bin в папку /boot
Добавьте такие строчки в файл lilo.conf:
И выполните команду lilo для обновления конфигурации.
Установка с использование GRUB / grub4dos
Скопируйте файл plpinstc.com в папку /boot
В файл menu.lst впишите следующие строки:
title PLoP Boot Manager Install
root (hd0,0)
kernel /boot/plpinstc.com
Для запуска Plop без его установки:
Скопируйте файл plpbt.bin в папку /boot
В файл menu.lst впишите следующие строки:
title PLoP Boot Manager
root (hd0,0)
kernel /boot/plpbt.bin
Конфигурирование Plop:
Настройка производится путём патчинья самого загрузчика Plop с помощью утилиты plpcfgbt
Например, если Вам нужно сделать загрузку с usb устройства и без лишних вопросов, то введите такую строку:
plpcfgbt.exe stm=hidden cnt=on cntval=1 dbt=usb plpbt.bin
Полный список опций можно посмотреть в файле 1README.TXT в директории с программой.
А теперь рассмотрим реально полезный пример использования Plop:
Задача:
1) Получить USB 2.0 или близкую к нему скорость на тех материнских, которые работают с USB 2.0 только в загруженной ОС, а на этапе загрузки выдают USB 1.1
2) Загрузиться в PCI USB 2.0 внешнего конроллера.
Решение:
1) Устанавливаем Plop на ваш носитель информации, я решил воспользоваться свой BootFlash с Grub4DOS в качестве загрузчика.
Общая схема загрузки будет выглядеть так:
Grub4DOS (usb1.1) => Plop => Grub4DOS (usb 2.0)
Сохраняем и пробуем.
Так-же можно сделать загрузку iso образа через RAM:
Скопируем ISO образ в корень диска, в файл menu.lst впишем следующие строки:
Сохраняем и пробуем.
2) В этом случае мы просто устанавливаем Plop на наш HDD,CD-ROM диск или дискету и в качестве устройства выбираем USB
Plop автоматически просканирует все USB порты и загрузить Ваш LiveUSB накопитель.
Думаю для ознакомления пока-что достаточно.
Возможно в будущим я продолжу публиковать информацию по этому замечательному загрузчику.
Boot manager для 486-го компьютера
Всё началось с того, что меня несколько расстраивало отсутствие возможности загружаться с дисковода на старой плате Socket 3. CD-приводы в то время ещё не были распространены и разработчики BIOS даже не задумывались о предоставлении такой опции. Да и операционные системы распространялись на дискетах. Чуть позднее, когда ОС (в основном конечно Windows) стало удобнее устанавливать с диска, чем с пары десятков дискет, придумали так называемые загрузочные floppy, содержавшие драйвер дисковода и передававшие ему управление непосредственно. Но это на мой взгляд костыль и некрасиво. Я начал искать более изящное решение и даже в какой-то момент собирался купить SCSI-контроллер за много денег и привод к нему, но нашлась альтернатива.
Этой альтернативой был Plop. На самом деле я даже не задумывался об использовании загрузчиков, но когда мне сказали про Plop, я решил, что это весьма здравая идея. Он умеет загружаться из кучи источников и загружать практически любые устройства, кроме usb-дисководов. Кроме того, он имеет удобный интерфейс и множество настроек. Подробнее почитать о нём можно на официальном сайте.
Оставалось только решить с чего загружать Plop. Самым очевидным вариантом была дискета, но это снова костыль. А больше компьютер (не считая диска, естественно) ни с чего грузиться и не умеет. И вот тут на помощь пришла, как ни странно, сетевая карта.
BootROM и с чем его едят
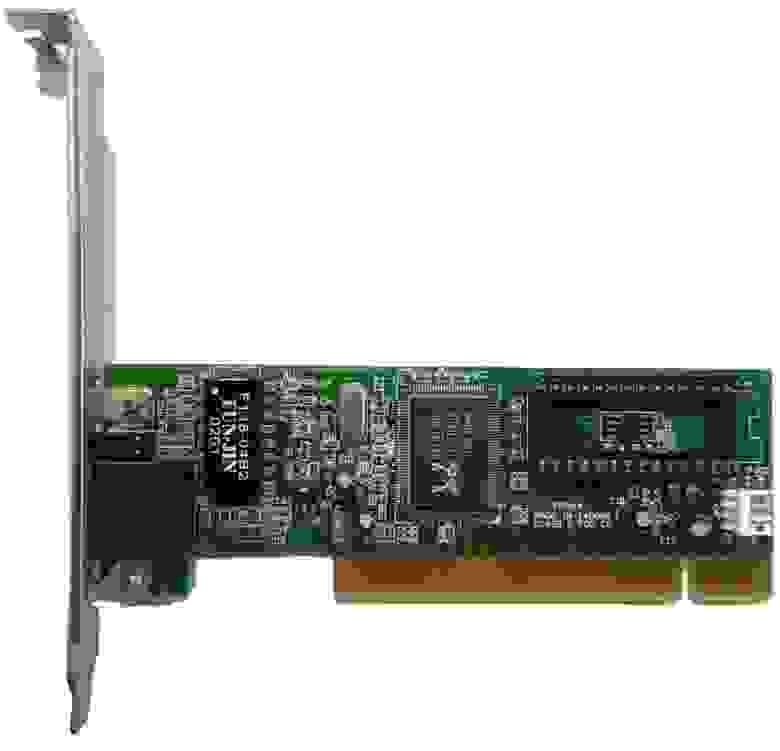
Да, да, сетевая карта. Дело в том, что некоторые из них имеют функцию сетевой загрузки с некоторого сервера и для этого несут на себе свой собственный BIOS. В моём случае это карта Realtek rtl8139.
Панелька предназначена для микросхемы памяти объёмом до 64 килобайт. Никто не заставляет записывать именно BootROM, это может быть любой код. Содержимое ПЗУ просто исполняется после загрузки основного BIOS. Так вот, Plop умеет загружаться с сетевой карты, но для этого его нужно подготовить.
Непосредственная настройка и установка
Начнём с конфигурации загрузчика. В этом нам поможет готовая программа, которую можно взять здесь. Я использовал GUI-версию. В ней нужно выбрать бинарный файл, предназначенный для записи в OptionROM. В конфигурации я сразу переключил режим вывода на текстовый (потому что графический сильно тормозил), отключил анимации. Для удобства использования лучше поставить галочки INT19 и Startup Hotkey. Теперь Plop будет загружаться только при нажатии комбинации Ctrl+A, практически как Boot Menu в современных компьютерах. По вкусу можно установить таймер и устройство по умолчанию.
Теперь можно переходить к прошивке. Я использую программатор MiniPro, но подойдёт любой другой, который поддерживает EEPROM и Flash до 64 килобайт. ПЗУ можно взять 27, 28 или 29 серий нужного объёма. Процесс прошивки проходит как обычно. Выбрать микросхему, выбрать образ и нажать на кнопку записи.
После всех этих действий остаётся вставить микросхему памяти в панельку на карте, а карту вставить в слот на материнской плате. Единственное, возможно потребуется включить BootROM в конфигурации самой карты. Я сделал это с помощью программы для DOS, поставляющейся вместе с драйвером.
Plop Boot Manager
The Plop Boot Manager is a small program to boot different operating systems. The boot manager has a built-in ide cdrom and usb driver to access that hardware without the help/need of a bios. You can boot the operating systems from hard disk, floppy, CD/DVD or from USB. You can start the boot manager from floppy, CD, network and there are many more ways to start the boot manager. You can install the boot manager on your hard disk. There is no extra partition required for the boot manager.
Programming language: Assembler
Software developer: Elmar Hanlhofer
Overview of install/start modes
| Hard disk installation | The boot manager will be installed as primary boot manager to your hard disk. No extra partition and required. The boot manager will be in the first sectors of your hard disk before the first partition begins. The boot manager starts even when no operating system exists. |
| Start from external media Floppy CDROM/DVD USB drive | It’s not required to install the boot manager to your hard disk. You can start it from those media and use the boot manager with some limitations. |
| Start from other boot managers LiLo Syslinux Grub Grub4Dos Grub2 Windows boot.ini Windows BCD | You can still use your preferred boot manager and additionally use features from the Plop Boot Manager (like boot the usb drive. ). The boot manager can run in hidden mode, so you have for example an entry in your preferred boot manager to boot the usb drive and when you use this entry then it starts immediately without any additional menu. This can be useful for the usb boot function. |
| Start from network | With help of pxelinux it’s possible to start the boot manager from the network. |
| Start from your bios as option rom | You can store the boot manager as option rom in your bios. There is no need for any hard disk or anything else to start the boot manager. It can be used as PNP part of your bios or the boot manager can hook the INT19 to take control as first boot device. |
Features
Screenshots
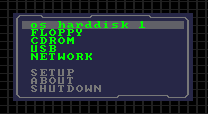
Main menu (text mode)
MBR partition edit
MBR Install Program
Licence
The Plop Boot Manager licence conditions:
This licence conditions are also used for the boot manager tools that are written by Elmar Hanlhofer and not released under the GPL.
¹ You can add the tools to non-profit products for free.
Example: You sell a CD and charge only the price for the blank CD without the work to create the final CD (and so on).
Download
| plpbt-5.0.15.zip | 2013-04-15 | Plop Boot Manager 5.0.15 |
| plpbt-5.0.14.zip | 2012-02-11 | Plop Boot Manager 5.0.14 |
| plpbt-5.0.13.zip | 2011-08-14 | Plop Boot Manager 5.0.13 |
Tools
| plpbtrom-0.6.zip | 2011-08-14 | Create a PCI Option ROM |
| plpbt-createiso.zip | 2010-06-08 | Create custom boot manager cd’s |
| plpcfgbt-0.11.zip | 2012-02-03 | Tool to configure the boot manager file plpbt.bin (Windows/Linux) |
| plpdisd-0.2.zip | 2010-10-16 | Deactivate the USB driver under DOS |
| plpchk-0.1.zip | 2010-10-14 | Detect the USB driver under DOS |
| plpmkboot-0.1.zip | 2012-02-03 | plpbt.bin native FAT boot |
The Boot Manager
2. Main menu
In the main menu you see all visible profiles to boot an operating system. You can start an operating system from floppy, cd/dvd, usb or network. You can go to the setup of the boot manager, partitions and profiles. If your bios supports APM, you can shut down your computer.
2.1. Main menu hotkeys
1-9 Boot profile q Quick boot, open a list of all possible hardcoded partitions to boot w Write MBR with the profile settings, but do not boot f Boot floppy c Boot CD/DVD u Boot USB n Network boot
Special additional keys for USB boot:
Press SHIFT-u to force USB 1.1
Press CTRL-u to wait for a key press before starting the operating system. When a drive was found, then you can press «s» to skip the device or you can boot from the drive.
Press ALT-u to wait for a key press before detecting the usb device type. When a device was found, then you can press «s» to skip the device or you can boot from the device when it’s as mass storage device.
Difference CTRL-u and ALT-u:
- When you use CTRL-u and the boot manager finds an usb device, then the boot manager identifies it. Because of the stripped down usb implementation, it’s possible that the boot manager sometimes hangs on some computers. With ALT-u, the identification of the usb drives happens when you press enter. When you press «s», then the boot manager skips the device and it should not hang.
3. Setup
3.1. Partitions
Edit label
You can change the label for the partition. This label is used in the boot manager. The maximum length is 16 chars.
Select Device
Here, you choose the hard disk of the partition.
HDA = Hard disk 1
HDB = Hard disk 2
HDC = Hard disk 3
HDD = Hard disk 4
Partition ID
There are 2 ways to set the ID of a partition.
1. Enter partition ID
You can enter the hexadecimal value for the partition.
2. Select ID from list
Edit MBR/Import data
This is used to change the values of partitions in the MBR.
BP means boot manager partition. This values are stored in the boot manager.
P1-P4 this are the current values of the primary partitions in the MBR.
Clear partition data
Clearing the data means clearing of the partition data in the boot manager. The data on the partition itself is unchanged.
Reset changes
Use it if you changed something and you want to restore the whole values of the partition in the boot manager. This is possible until you close the partition edit window.
3.2. Profiles
Profiles are used to start different operating systems from different hard disks and partitions. It’s also possible to detect changes in the MBR made by other software and import or forget the changes.
If you have an operating system installed and you install the boot manager, the installer creates a profile to boot the current operating system.
Edit label
You can edit the label of the profile. This label is shown in the main menu. It’s useful to use a label to see what operating system is going to boot. The maximum length is 16 chars.
Show in main menu
With this option you select if the profile is shown in the main menu or not. Only visible profiles can be booted. It also has effects on the default profile in the boot manager setup.
Linked partitions
You select from which hard disk, partition and bios device number you want to boot with this profile. You can also select what partitions or cleared partitions should be used for the MBR.
Configure partition entries
There are 3 states for a partition entry
1. a selected partition
If another software changes this entry in the MBR, the boot manager detects this change at the next startup. You can choose if you want to import the new values or forget them.
2. don’t touch
The partition entry in the MBR will not be changed from the boot manager. That is the default setting.
If a software changes this entry in the MBR the boot manager cannot detect this change.
3. cleared
The boot manager set’s this entry to 0 in the MBR. An operating system cannot detect that there is/was a partition.
Partition programs will say this is unallocated space! Do not partition this space! You can lose data if you do it wrong.
b set boot partition. You select, what partition you want to boot with this profile. The boot manager set a bios drive number automatically. It’s possible to change it with another key.
c clear partition. You set this entry to «cleared» and the boot manager clears this entry in the MBR when you boot this profile.
d don’t touch. You set the entry to don’t touch and the boot manager does not change this entry when you boot this profile.
e edit boot flag. The boot flag has the bios drive number used by the boot sector routine. In some cases it’s required to change this value.
r remove boot flag. Here, you remove the boot flag from the profile.
Clear profile data
You can clear the profile data in the boot manager. The data in Partitions are not changed.
Reset changes
Use it if you changed something and want to restore the whole values of the profile in the boot manager. This is possible until you close the profile edit window.
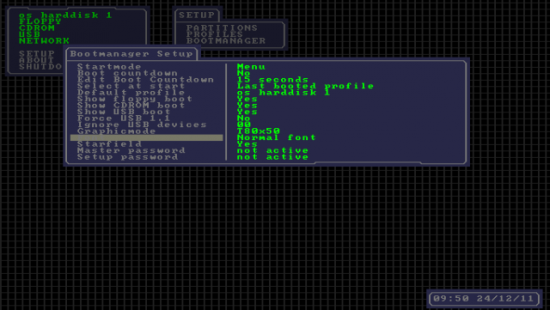
3.3. Boot manager
Startmode
Boot countdown
You can enable and disable the countdown.
If the boot countdown is enabled, the boot manager waits the given time and starts after the countdown the last used profile or the default profile, depending on your settings.
Edit boot countdown
Choose between 1 and 99 seconds.
Select at start
At start, the boot manager set the bar to the selected option. This works for the hidden start mode too.
You have the following options
1. Last booted profile
2. Default profile
3. Floppy
4. CDROM
5. USB
Default profile
You can select the default profile from a list of all visible profiles.
Show floppy boot
Show the floppy boot option in the main menu.
Show cdrom boot
Show the cdrom boot option in the main menu.
Show usb boot
Show the USB boot option in the main menu.
Force USB 1.1
Use USB 1.1 controller even if there is a USB 2.0 controller.
Mode 1: Ignore the EHCI Controller
Mode 2: Setup EHCI Controller and set all ports to the companion host. Some controllers need this option to force usb 1.1.
Use Mass Stor Dev
Use Mass Storage Device. Boot the X mass storage device that was found. Other devices are ignored.
Text mode after boot
You can select the text mode during the startup of an operating system. Choose between «don’t change» and 80×50.
Graphicmode
Select the screen resolution in the boot manager. Choose between text mode 80×50 and graphic mode 640×480, 800×600, 1024×768, 1280×1024.
Zoom animation
Enable and disable the window animation.
Select the boot manager font or the bios font.
Starfield
Enable and disable the starfield animation.
Master password
Setup the master password. Disable the boot manager password protection with an empty password.
Setup password
Setup the setup password. Disable the boot manager setup password protection with an empty password.
Install to the hard disk MBR (Master Boot Record)
You can install the boot manager to the MBR of your hard disk. When you do that, then the boot manager is the first program that is started when you boot from the hard disk. That means the boot manager is started before any operating system has been started. This installation has many benefits. Some features are only available when the boot manager is installed to the MBR.
As simple alternative to the MBR installation, it’s easy to add the boot manager to an existing boot manager. See here.
Warning Linux users: Install LILO or GRUB to the boot sector of your Linux instead of the Master Boot Record (MBR). The Plop Boot Manager is not a Linux loader and cannot start Linux without LILO, GRUB, Syslinux and similar! See Linux Boot Managers.
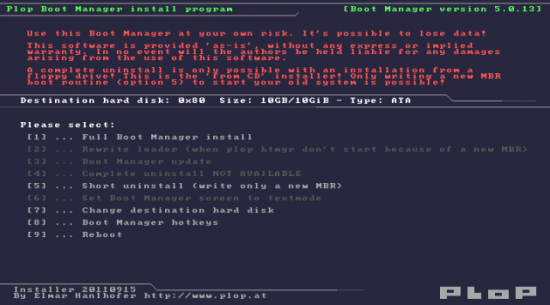
1. The install program
There are 2 versions of the install program. Basically both versions do the same. The only difference is that plpinst.com creates a backup file plpback.bin to restore hard disk sectors for a complete boot manager uninstall. The second version plpinstc.com skips the backup part. You have to use the second version for installation from write protected media like CD’s or when you install from network or any other boot manager.
1.1 Program functions
1. Full boot manager install
With this option you install the boot manager to your hard disk. If you have an installed operating system, then the install program creates a profile for you to boot this operating system.
With the installation from floppy, the install program makes a backup of the sectors where the boot manager will be installed. The install program writes the backup to the floppy disk. With this backup it’s possible to remove the boot manager completely from your hard disk. If you use the CD installation, then it’s not possible to restore the sectors. In this case the uninstall routine creates a new MBR to boot the current operating system. The partition table data won’t be changed.
2. Rewrite loader
3. Boot Manager update
With this, you can update the boot manager. But only updates with boot manager v5 are working.
4. Complete uninstall
Warning, this option is only available with the installation from floppy.
The install program takes the backup that was saved on the floppy disk and writes it back to the hard disk.
Warning, if you changed anything with the partition table, then don’t use this option!
5. Short uninstall
With this option, the program writes a new MBR to start the current operating system. The partition table will be unchanged.
6. Set Boot Manager screen to text mode
Configures the Boot Manager to start in text mode.
7. Change destination hard disk
Set destination hard disk to install the boot manager.
8. Boot Manager hotkeys
9. Reboot
The computer will be restarted.
2. Uninstall
When you installed the boot manager to the MBR, then you can remove the boot manager in the same way that you used to install the boot manager, but you have to use the option 4 or 5 in the install program. The option 4 is only available when you install from floppy.
When you don’t want to use the install program to remove the boot manager, then you can use any other program that writes a new program to the MBR. Example FIXMBR, or «fdisk /mbr» and so on. Or you install another boot manager to the MBR.
3. Methods to start the install program
3.1. Floppy
You create the install floppy with a floppy disk image. A floppy disk image is a file that contains every sector of the floppy disk. You cannot copy the image file on a floppy disk like a common file. It’s required to use a special program that writes sector per sector of the image file to the floppy disk sectors. There are many programs available to do this.
Download the current boot manager plpbt-5.0.15.zip. Extract it to get the floppy disk image. You find the disk image in the install directory. The name of the file is plpbtin.img
How to create the floppy:
Windows: Write the disk image with the program rawwritewin to the floppy disk
Linux: dd if=plpbtin.img of=/dev/fd0
3.2. CD
Download the current boot manager plpbt-5.0.15.zip. Extract it to get the iso file. You find the iso file in the install directory. The name of the file is plpbtin.iso
Notice: The CD installer makes no backup for a complete uninstall. See The install program.
You can use Nero, or the free program CDBurnerXP, or any other program that can burn ISO images.
cdrecord is the linux program to burn ISO images to a CD.
3.3. DOS
Download the current boot manager plpbt-5.0.15.zip. Extract it to get the install program. In the install directory there are 2 install programs ( plpinst.com and plpinstc.com ) for using under DOS.
plpinst.com creates a backup file plpback.bin for a complete boot manager uninstall. plpinstc.bin makes no backup. Use plpinstc.com for write protected media like CD’s.
3.4. Windows boot menu (NT, 2K, XP, VISTA, Win7)
Note: plpgenbtldr and contig are no longer required.
3.5 Syslinux, Isolinux, Extlinux
Download the current boot manager plpbt-5.0.15.zip. Extract it to get the boot manager install program. You find the install program plpinstc in the install directory.
Add the following lines to the config file
Copy plpinstc to the same directory where the config file is.
You start the install program when you select it from the menu or you enter plpinst at the Syslinux command prompt.
3.6. LILO
Download the current boot manager plpbt-5.0.15.zip. Extract it to get the boot manager install program. You find the install program plpinstc.com in the install directory.
Add to your /etc/lilo.conf the following
Run lilo to update lilo.
3.7. GRUB / grub4dos
Download the current boot manager plpbt-5.0.15.zip. Extract it to get the boot manager install program. You find the install program plpinstc.com in the install directory.
Add to your /boot/grub/menu.lst the following
When you reboot, you should be able to choose the install program from your grub menu.
Info: You have to choose the correct root settings in your configuration or you get a «Error: file not found». See also this Forum entry.
3.8. GRUB2
Download the current boot manager plpbt-5.0.15.zip. Extract it to get the boot manager install program. You find the install program plpinstc.com in the install directory.
When you reboot, you should be able to choose the install program from your grub menu.
Info: You have to choose the correct root settings in your configuration or you get a «Error: file not found». See also this Forum entry.
3.9. From network
A better documentation comes when I have more time. Meanwhile use the documentation of Plop Linux.
You need for booting over network a DHCP, TFTP server and the program pxelinux.
3.10. Native from a FAT file system
Download the current boot manager plpbt-5.0.15.zip. Extract it to get the boot manager install program. You find the install program plpinstc.com in the install directory.
Then use the program plpmkboot to make the drive bootable to start plpbt.bin.
Linux example: plpmkboot /dev/sdb1
Windows example: plpmkboot F:
Hint: Do not use the other install program plpinst.com except on FAT12 formatted drives.
1. Floppy
A floppy disk image is a file that contains every sector of the floppy disk. You cannot copy the image file on a floppy disk like a common file. It’s required to use a special program that writes sector per sector of the image file to the floppy disk sectors. There are many programs available to do this.
How to create the floppy:
Windows: Write the disk image with the program rawwritewin to the floppy disk
Linux: dd if=plpbt.img of=/dev/fd0
You can configure the plpbt.bin on the floppy with plpcfgbt.
2. CD (LiveCD)
You can use Nero, or the free program CDBurnerXP, or any other program that can burn ISO images.
cdrecord is the linux program to burn ISO images to a CD.
3. Windows boot menu (NT, 2K, XP, VISTA and Win7)
Note: plpgenbtldr and contig are no longer required.
4. Syslinux, Isolinux, Extlinux
Add the following lines to your config file
Copy plpbt.bin to the same directory where the config file is.
You start the boot manager when you enter plp at the Syslinux command prompt.
You can configure the file plpbt.bin with plpcfgbt.
5. LILO
Add to your /etc/lilo.conf the following
Run lilo to update lilo.
You can configure the file plpbt.bin with plpcfgbt.
6. GRUB / grub4dos
Add to your menu.lst
Info: You have to choose the correct root settings in your configuration or you get a «Error: file not found». See also this Forum entry.
You can configure the file plpbt.bin with plpcfgbt.
7. GRUB2
Example file /etc/grub.d/40_custom
When you reboot, you should be able to start the boot manager from your grub menu.
Info: You have to choose the correct root settings in your configuration or you get a «Error: file not found». See also this Forum entry.
You can configure the file plpbt.bin with plpcfgbt.
8. From network
A better documentation comes when I have more time. Meanwhile use the documentation of Plop Linux.
You need for booting over network a DHCP, TFTP server and the program pxelinux.
9. Native from a FAT file system
Copy plpbt.bin to the FAT formatted drive.
Then use the program plpmkboot to make the drive bootable to start plpbt.bin.
Linux example: plpmkboot /dev/sdb1
Windows example: plpmkboot F:
Uninstall the boot manager
Uninstalling the Plop Boot Manager depends on where it is installed.
1. MBR
Restart the install program and choose the option 5 to write a fresh MBR program and remove the Plop Boot Manager start routine.
When you don’t want to use the install program to remove the boot manager, then you can use any other program that writes a new program to the MBR. Example FIXMBR, or «fdisk /mbr» and so on. Or you install another boot manager to the MBR.
2. Windows Boot Menu
3. LiLo, Grub and other boot managers
Just remove the boot manager entry and update the configuration when its required for the program.
Create your own ISO file with your modified plpbt.bin
How to use with Windows
How to use with Linux
plpcfgbt-0.11.zip is a tool to configure plpbt.bin. This program is available as source code for Linux and Windows. You start the program from a command shell. If you run the program without parameters then you will see the help information.
Infos about int19h see here.
The hotkey option is useful with CD’s or ROM’s. You get the info to press CTRL-A to start the boot manager. If you don’t press it, the booting continues without the boot manager.
Examples
Print current settings:
Configure hidden boot and boot the usb drive:
plpcfgbt stm=hidden cnt=on cntval=1 dbt=usb plpbt.bin
or
plpcfgbt hiddenusb plpbt.bin
plpbt.bin parameters
List of supported parameters
| Parameter | Meaning |
| hiddenusb | is the short version of «stm=hidden cnt=on cntval=1 dbt=usb» |
| hiddencdrom | is the short version of «stm=hidden cnt=on cntval=1 dbt=cdrom» |
| usb1=1 | Force USB 1.1 Mode 1 (ignore the EHCI controller) |
| usb1=2 | Force USB 1.1 Mode 2 (force EHCI ports to usb 1.1) |
| vm=text | Switch to text mode |
| fnt=bios | Switch font to bios font |
| int19h=on | Use INT19h instead of booting usb |
| showextended=yes | Show extended partitions in the main menu |
Create a PCI boot manager option ROM (save in bios)
You can create a pci option rom file with plpbtrom-0.6.zip. You can store the option rom in your bios or to the rom of a network card and run it from there.
Examples
Special parameters
-forceINT: This forces the boot manager to hook the INT 19h/INT 18h. If you have a PNP bios, then the boot manager does not use the PNP bios feature of the boot device sequence. The boot manager will be started before any boot device is tried (when INT 19h mode is used) or the boot manager is the last program that is started when all boot devices failed to boot (when INT 18h mode is used).
-INT18: Hook INT18h instead of INT19h. INT19h is the default mode.
Files
Difference plpbtrom.bin and plpbt.bin
plpbtrom.bin gives the control of the boot process back to the bios with a far return if you press esc. plpbt.bin makes a reboot with int 19h.
Passing parameters to the boot manager with the linux kernel command line is not supported by plpbtrom.bin
You can configure plpbtrom.bin like plpbt.bin with plpcfgbt. You can enable/disable a hotkey to start the boot manager.
How to test a ROM
You can test your rom file with the free virtual machine qemu.
If you have no hard disk image file then take one from the qemu download page or use a floppy image.
How to flash an AMI bios
Do this at your own risk! This can damage your pc.
Download the Ami bios flash utility and save your current bios. AMI Homepage
It’s a DOS program, run the following command from a DOS floppy to save your bios
Load the file bios.rom
Click on it that it’s marked.
Click at the Replace Tab
Load as Module file the plpbt.rom file.
Press the Replace button
Press the Save ROM as and give it the name mybios.rom
Now comes the dangerous part. Flashing the bios.
I suggest setting the bios to the default settings and save it. Then boot from a dos floppy and run
Do not turn off the pc during flash. After the flash has completed, go to the bios and do again a reset to the default settings.
If all is ok, you should be able to configure the bios and start the boot manager during the boot process.
How to flash an AWARD bios
Do this at your own risk! This can damage your pc.
Search the file cbrom in the web. There are different versions, not all will work with your bios file, so you have to test it with different versions.
Run cbrom bios.rom /d
This should list all parts of the bios rom. I cannot give you the command to replace the rom. None of the cbrom programs where able to display the content of my bios rom file. You have to test it by yourself.
If all is ok, you should be able to configure the bios and start the boot manager during the boot process.
plpbt4win
plpbt4win makes it easy to add/remove the boot manager from the windows boot menu. The program can work with the boot.ini and with bcdedit. It automatically detects the required method. You can use it as batch file or run it with an built-in command line. You find plpbt4win in the Windows directory of plpbt-5.0.15.zip.
Feature list
Command line interface, ideal for batch programs and a gui frontend.
Built-in command line.
Works with boot.ini and bcdedit.
Can list, add and remove windows boot menu entries.
You can easy use different boot manager binary files. For example, one windows boot menu entry is the default boot manager file and another entry is configured to auto boot usb.
2 batch files are included. InstallToBootMenu.bat and InstallToMBR.bat. The windows user must only start the batch file and everything is done by the batch file. The user must only reboot to see the new boot menu entries. Those batch files can also be used as example how to use plpbt4win.
Help for batch mode
Batch mode examples
List boot menu entries: plpbt4win /B /L
Create loader: plpbt4win /B /C
Create custom named loader: plpbt4win /B /C c:\plop\plp.ldr
Add an entry: plpbt4win /B /A «The Plop Boot Manager is here»
Remove an entry, first use /L to get the ID and then: plpbt4win /B /R 3
Create loader and add entry at once: plpbt4win /B /C /A
Help for built in command line
Start plpbt4win without parameter.
Note for Windows XP error
Windows could not start because the following file is missing or corrupt:
\system32\hal.dll
Solution: Rename the file ‘plpbt4win.ldr’ to ‘plpwin.ldr’. Set the new file name in the ‘boot.ini’.
plpgenbtldr
plpgenbtldr is outdated and no longer supported. Use plpbt4win.
To remove entries from the windows boot menu use either plpbt4win or
Open a command prompt as administrator.
Run » bcdedit /v » to list all entries.
Run » bcdedit /delete
Many old laptops are having one or two CardBus slots. The boot manager can act as USB PC-Card enabler and the boot manager makes it possible to boot from the USB PC-Card. When your laptop has only USB 1.1, then you can speed up the boot process with an USB 2.0 PC-Card. When your laptop has only one USB port, then you are able to get more USB ports with an USB PC-Card.
You find the boot manager with the CardBus driver in the pcmcia directory of plpbt-5.0.15.zip.
The boot manager initializes the CardBus during the boot manager startup. This means, the PC-Card must be plugged in during the boot manager start! I do this during the program start, because then you have an initialized and ready to use PC-Card regardless if you boot from usb or not. When you have a DOS USB driver (for OHCI and EHCI) then you are able to use it with the PC-Card and you don’t need a extra CardBus driver.
During the boot manager startup you will see some infos about the CardBus init process. When you want to read it, then press the CTRL key during the boot manager start.
My CardBus driver works on many machines, but it does not work on all.
Because of the additional CardBus driver size, I had to remove the IDE Cdrom driver (only) from the pcmcia hard disk boot manager version.
plpbt.bin has all drivers included.
USB info
DOS and the USB driver
1. The Boot Manager as USB hard disk driver for DOS
I know this is very special. Maybe it’s useful for some people. You have to configure the plpbt.bin with plpcfgbt to use int19h instead of booting the operating system.
plpcfgbt int19h=on plpbt.bin
If it works for you then use plpcfgbt int19h=on stm=hidden cnt=on cntval=1 dbt=usb plpbt.bin
2. Disable the USB driver
If you run DOS and the Plop USB driver is loaded, then you can disable the USB driver with plpdisd-0.2.zip. When you disable the driver, then you are able to load other DOS usb drivers.
You can run plpdisd from config.sys
It’s also possible to run it from the autoexec.bat or command line.
3. Detect the USB driver under DOS
Detect the USB driver
1. Detect the USB driver with Syslinux
Icecube wrote the module ifplop.c32 for syslinux to detect the plop usb driver
ifplop.c32 is part of syslinux since version 4.01.
ifplop.c32 module page: http://syslinux.zytor.com/wiki/index.php/Ifplop.c32
You find some driver detection info’s here.
2. Detect the USB driver under DOS
With the program plpchk-0.1.zip you are able to detect the plop usb driver. You can use it in the config.sys, in a batch program or from the command line. The program is able to create a file when the driver is installed, or delete a file when the driver was not detected. According to the existence of the file you can do some actions. For batch files you can use the return value of the error level. The program makes no screen output when you use the /h parameter.
You find some driver detection info’s here.
Hidden partition / Cleared partition
Hidden partition / Cleared partition
There is a important difference between «hidden» and «cleared» partitions.
Hidden Partition: Operating systems, backup solutions and so on can see them but they ignore them. I would say, this is a pseudo hidden partition.
Cleared Partition: No program (except the boot manager) knows that there is/was a partition defined in the MBR. This is really hidden. It looks like unallocated space for every program. That means no other program can access the data on that partition (with some work and searching the hard disk there are still ways to access the data). There is a risk, if you repartition the hard disk, you will overwrite your invisible partition and all data on it if you do it wrong.
Example: Hide a partition
This is an example: A partition should be visible in one profile and hidden (and not cleared) in another profile
Let’s say you want to have the second partition on HDA (HDA2) on one profile visible and on another hidden (and not cleared).
Use an empty entry in partitions. Give it the label «hidden hda2».
Select the device HDA.
Go to «Edit MBR/Import data».
Move the cursor to P2 and press «s». Now move up to «BP» and press «p».
Press ESC and go to «Partition ID». Choose «Select from list». Choose the hidden version of your partition.
Press ESC and save your changes.
Go to «profiles».
Now you can assign the «visible» version of your partition to one profile and the «hidden» to another profile.
Linux Boot Managers to the boot sector
Examples
1. Video dual boot install Windows XP and Windows XP
Download demoinstall.wmv (demoinstall.zip). The quality is not the best but you see all required steps. I hope it’s useful.
2. Windows XP and Windows Vista dual boot with hidden (cleared) partitions
The goal is to install Windows XP on the first partition and Windows Vista on the second partition. I want that no windows has access to the partition of the other Windows. There should be a third partition that will be used as shared partition. Both Windows have access to this partition.
There are many ways to do this. I will describe one way.
It works only with the MBR installation!
What should be the result
Basic conditions
The description
Install Windows XP
At first install Windows XP. Create with the Windows installer a partition with the size you want. I use a 10GB partition. Install Windows XP on this partition.
Setup Partitions
When you installed your Windows, go to the Disk Management and create a second primary partition for Vista and a third primary partition for the shared data.
Install the boot manager
Now comes the boot manager part. Boot from the boot manager install floppy or CD. Install the boot manager to the hard disk and then reboot.
Configure the Windows XP profile
The boot manager created a profile called «os harddisk 1» to boot Windows XP. It also imported the 3 primary partitions. The names are HDA1, HDA2 and HDA3.
Configure the Windows Vista profile
Install Window Vista
Now you should have two bootable Windows on your hard disk and they don’t know from each other. You can share data between both with the shared partition.
Windows Vista on the second hard disk
3. Dualboot Windows XP and Windows 7
Here are short instructions for a complete new installation of your pc with dualbooting WinXP and Win7. It doesn’t matter if you use 32 or 64 bit versions. Take care, all data on your pc will be deleted!
Boot the Win7 install DVD. Remove all partitions from the hard disk. Create a partition for Win7. The install program will create 2 partitions. One with about 80MB for the Win7 boot files and a second partition with the Win7 files. Create an additional partition for WinXP. Now you see 3 partitions. Install Win7 to the second partition. After the Win7 installation is complete, install the Plop Boot Manager. After the Boot Manager installation go to the Boot Manager Setup, then Profiles, then «OS HARDDISK 1». Change the name to «Win7». Go to linked partitions and press enter on the first position of HDA and select HDA1, on the second select HDA2 and on the third press «c» for cleared. Now leave the profile settings for Win7. Use now an empty profile to create the WinXP profile. Give it the name WinXP, visible in main menu «yes». In linked partitions select for HDA on the first position HDA3, press «b» to set the boot flag on the first position. On the second press «c» to set it cleared. On the third press «c» to set it to cleared too. Go to the main menu and press enter on WinXP. You will be not able to boot this partition because XP is not installed currently. If you get the message about invalid boot signature, then press «n» to abort. Now boot the WinXP install CD. You should see now only one partition. Install WinXP there. After the installation completed then start the Plop Boot Manager install CD and use «Rewrite loader». Reboot, the boot manager will tell you about partition changes. Press «y» to import the new values. Now you should be able to boot both systems.
NOD32 Virus report
NOD32 reports a MBR virus after the Boot Manager MBR installation. It’s a false report. This problem was fixed but with the new NOD32 versions it’s back.