Что такое deadlock sql
Как мы ловим Deadlock`и на PostgreSQL и чиним их
Предисловие
Ситуация: есть высоконагруженная мета-игра для наших танков под названием Глобальная карта. Эдакая пошаговая настолка для команд, где бои происходят в реальном танковом клиенте. В пиковые часы на карте несколько тысяч руководителей кланов производят игровые действия: атакуют друг друга, перемещают дивизии, покупают, продают, грабят корованы. Помимо этого, существует десяток сервисов, которые также могут вносить изменения в игровую ситуацию: подкидывают деньжат, штрафуют, добавляют игроков в клан и прочее.
Всё это неизбежно приводит к дедлокам. Так вот, хочу вам поведать историю о том, как мы эти периодические проблемы держим в допустимых рамках.
Немного о внутреннем устройстве бекенда
Часть 1: Мониторинг
Как проявляется Deadlock
Когда у нас возникает Deadlock, то падает исключение следующего вида:
ERROR: deadlock detected
DETAIL: Process 18293 waits for ShareLock on transaction 639; blocked by process 18254.
Process 18254 waits for ShareLock on transaction 640; blocked by process 18293.
HINT: See server log for query details.
CONTEXT: while updating tuple (0,9) in relation «users»
Первое, на что следует обратить внимание, — это строчка:
HINT: See server log for query details.
Действительно, если мы посмотрим серверные логи, то увидим для этого же места следующее:
ERROR: deadlock detected
И дальше конкретику:
DETAIL: Process 18293 waits for ShareLock on transaction 639; blocked by process 18254.
Process 18254 waits for ShareLock on transaction 640; blocked by process 18293.
Process 18293: update users set balance = balance + 10 where > Process 18254: update users set balance = balance + 10 where >
HINT: See server log for query details.
CONTEXT: while updating tuple (0,9) in relation «users»
И, наконец, запрос, на котором произошла ошибка:
STATEMENT: update users set balance = balance + 10 where >

Логирование запросов при этом не обязано быть включено.
Круто. Но первая глобальная проблема для любого более-менее серьёзного проекта — то, что у вас нет доступа к серверным логам вследствие политики безопасности. Иногда вообще нет никакого доступа. А иногда можно попросить участок, но надо ждать. Иногда это 30 минут, иногда день.
А хотелось бы получать такую информацию сразу. В особенности, если у вас в проекте есть Sentry, и большинство ошибок команда разработки получает сразу.
Как-то подкрутить сервер, чтобы он такую информацию выдавал обычным клиентам — нельзя. Вследствие политики безопасности разработчиков базы. Но, если у вашего пользователя к базе доступ обычный, без всяких там ограничений на выполнения служебных функций и без Row-Level security policies, то организовать себе доступ к подобной информации всё же можно.
Ручной захват
Мы можем преобразовать наши классы так, чтобы вручную получать похожую информацию. И даже больше. Для этого после отлова исключения о дедлоке, нам необходимо:
В данном случае у нас есть высокая вероятность того, что мы увидим какой именно запрос сломал нам транзакцию, вычислив его по PID и посмотрев текущий query.
Но бывает и так, что вычислив соединение по PID и посмотрев на query вы можете увидеть совсем не тот query, который устроил нам дедлок, а какой-нибудь следующий за ним по логике. Ведь пока вы ловили исключение и открывали соединение, нужный нам запрос для отлова мог и завершиться. Всё что мы можем здесь сделать — это работать через pgBouncer или его аналоги для минимизации времени установления соединения и использовать application_name.
application_name
Даже если вы получили тот запрос, который вызвал дедлок, у вас всё равно могут возникнуть трудности с пониманием, в каком месте логики он был вызван. И вот здесь на помощь приходит поле application_name. По умолчанию оно инициализируется не сильно полезной информацией, но его можно менять. А что если писать туда то место, откуда мы начинали транзакцию?
Вуаля. Теперь можно быстро открывать файлы в нужных местах и смотреть код.
| pid | application_name | state | query | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8613 | deadlock_test.py:10 | idle in transaction (aborted) | UPDATE users SET balance = balance + 10 WHERE RETURNING pg_sleep(1); |
| 2 | 8614 | deadlock_test.py:17 | active | UPDATE users SET balance = balance + 10 WHERE RETURNING pg_sleep(1); |
| 3 | 8617 | active | SELECT pid, application_name, state, query FROM pg_stat_activity; |
Думаем о серверных логах
Вся эта магия, описанная сверху хороша, но теоретически может не сработать. Иногда вам всё же не обойтись без серверных логов, поэтому необходимо сделать ещё два шага:
Часть 2: Как бороться с дедлоками
Обычно в таких разделах дают ссылки на документацию об уровнях изоляции транзакций, видах блокировок и предлагают думать и анализировать в разрезе своего приложения. Я тоже так сделаю, но позже. А сначала просто опишу как мы это делаем чаще всего, ибо так уже получилось, что дедлоки у нас очень похожи друг на друга.
Несколько практик избегания deadlock`ов
Частый случай №1: Классический дедлок
Самый наш частый случай следующий:
Всё что тут можно сделать: или выстраивать начисления в цепочку, но это медленно, или позволять начислениям падать и пробовать начислить чуть позже.
Частый случай №2: Сам себе злобный буратино (ССЗБ)
У нас походовая игра. Раз в ход происходит пересчёт баланса игроков, учитывая большое количество совершённых ими игровых действий. На время изменения баланса мы блокировали другие изменения через SELECT… FOR UPDATE. Хотя мы блокировали не сразу всех, а чанками по 100, всё равно иногда уходили в дедлок с процессом, который начисляет бонусы за бой, который не останавливается на время расчёта хода.
Так вот, оказалось, что мы были неправы. SELECT… FOR UPDATE — слишком мощная блокировка, необходимая только если выполняются 2 условия:
P2 в данной ситуации повиснет, поскольку мы даём СУБД понять, что запись с может перестать существовать. Однако в P1 мы не делаем ничего такого, только хотим защитить баланс клана от изменений. Поэтому, когда мы изменили FOR UPDATE на FOR NO KEY UPDATE, мы перестали ловить дедлоки.
Бонус №1
SELECT… FOR UPDATE в примере выше вызван явно. Но вы получите аналогичный эффект, если затронете своими изменениями уникальный ключ, на который ссылается внешний ключ из других таблиц. А любой UPDATE, который не затрагивает своими изменениями подобные ключи, вызовет блокировку аналогичную SELECT… FOR NO KEY UPDATE. Я вам рекомендую ознакомиться с этими особенностями в статье «Явные блокировки» в списке литературы ниже.
Бонус №2
Вернёмся к ещё одной любопытной детали из первоначальной ошибки:
CONTEXT: while updating tuple (0,9) in relation «users»
Что за тупл спросите вы? Это физический адрес строчки в таблице, из-за которой возник конфликт. Дело в том, что в каждой таблице есть служебные поля, которые запросом SELECT * не выбираются. Однако стоит явно указать к примеру ctid среди полей, как мы увидим этот самый тупл:
Пользы от него немного в случае дедлока, ибо разблокированный процесс скорее всего обновит конфликтную строчку, и у неё изменится этот ctid (поскольку любой UPDATE в PostgreSQL на самом деле INSERT, а старая строчка помечается как невидимая и позже будет удалена автовакуумом). Но знать стоит, вдруг когда-нибудь пригодится.
Deadlock, что за зверь, с чем едят?
Здравствуйте. Имею небольшой сервер на node.js+mysql. использую движок mysqljs. Сам сервер парсит данные раз в минуту с некоторых сайтов и складывает их в таблицу бд(таблица получается относительно небольшой, 8к строк и около 15 столбцов). А также делает выборку из бд в таблицу html. С некоторого времени стали появляться ошибки «Error: ER_LOCK_DEADLOCK: Deadlock found when trying to get lock; try restarting transaction». Погуглив, я понял, что необходимо повторить запрос и ошибка уйдёт. С конкретным запросом то оно вроде пропадает, но тут же появляется новая ошибка лока, уже с другим запросом.
Также гугл подсказал делать commit’ы. Но возникает вопрос. На движке mysqljs вроде как нет возможности отправлять сразу несколько запросов вида
И приходится открывать pool, и делать много connection.query() запросов один за одним. Всё это ужасно не удобно.
Есть ли какой-то деликатный способ обхода ER_LOCK_DEADLOCK на nodejs?
Есть ли способ сбросить непроведённые транзакции?
Почему возникают дедлоки? Из-за того что sql не успевает обрабатывать данные? Если да, то поможет ли, если я создам новую таблицу и часть данных перенесу туда?
p.s. забыл написать, проверяю статус через «SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS», там выдаёт 3.5к строк текста, в которых написано что 140 локов висит
Средний 3 комментария
Лентюй, спасибо, гуглить я и сам умею. Тем более доки на английском найти вообще ума не надо.
Я задал вопрос здесь, чтобы найти человека, который популярно на пальцах сможет объяснить, в чём проблема и как её решить.
Чтобы вы понимали, я с мускулом всего неделю работаю.
Судя по исходным данным, тут не коммиты с транзакциями писать надо, а просто почитать про составление sql-запросов.
Запрос типа
решит вашу проблему.
Код в топике я взял из гугла. Вот пример моего кода:
т.е. тут присутствует запрос с взятием из другой таблицы данных и записью в основную
Тем не менее, спасибо, что откликнулись
На сколько я могу предположить, у вас несколько Promise.all([clearTempLOOT(), clearAll_prices()]) одновременно срабатывает.
Складывал бы все записи во временную таблицу
Таблица temp_loot и есть временная. Перед каждой сессией она полностью очищается, потом туда закидываются данные, потом из неё данные перекидываются в all_prices.
Стек подсказывает, что проблема возникает при запросе
, который добавляет в общую таблицу все предметы(товары), которых нет в таблице temp_loot,
либо при запросе
который обновляет все цены в таблице all_prices, беря значения из temp_loot.
Вообще, изначально проект был построен на чтении и записи данных в файл. И в момент, когда что-то в многопотоке записывалось и считывалось одновременно возникала ошибка. Для её избежания и для оптимизации решил перейти на mysql, но по-видимому тут ещё больше проблем. Мне казалось sql умнее и сам умеет в очередь всё ставить.
Когда ещё была реализована запись в файлы, была идея создать небольшой сервер, на который бы посылались запросы с чтением и записью из файла, и этот сервер бы сам в очередь ставил запись и чтение. Чтобы только он считывал и записывал и тогда проблем не было бы. Но это довольно муторно. Судя по всему здесь придётся реализовывать что-то подобное?
Ну, смотрите.
в первом вашем запросе у вас сразу же дедлок, потому что вы пытаетесь вставлять в таблицу, и то, что вы собираетесь вставлять тут же у вас селектится.
По-хорошему, это делается иначе:
на name вешается unique индекс и производится вставка с игнором.
Типа такого:
SQLShack
What are SQL Server deadlocks and how to monitor them
Introduction
As a DBA, I’ve been, more than, confronted with performance problems. Sometimes, poorly written code or lack of indexes will generate blocking conditions that we refer to as a“Deadlock”. Due to their nature and like any similar blocking situation, deadlocks can have a direct impact on user experience and the more they occur, the bigger the impact.
This article is the first one of a series that will focus on deadlock issues and reporting. After reading this article you will be able to explain how a deadlock can occur and how we can get extended information about this deadlock so that we will be able to diagnose and take the appropriate actions. These actions would lead to either a lower occurrence frequency or a total disappearance of deadlock conditions.
So, in the following sections, we will try to understand, basically, what a deadlock is and how it occurs with a practical example in T-SQL. Then we will see that SQL Server actually has some tools to help detect their occurrences and get everything we need to find and fix it, although the solution might be simpler said than done…
Basics understanding
Intuitive comprehension
So, what is a “deadlock”? Etymologically, it can be divided into two root words: “dead” and “lock”. We could intuitively understand it as a lock that leads to a dead end…
In relational database management systems, locking is a mechanism that happens every time. Actually, we can acquire a lock on different kind of resources (row identifier, key, page, table…) and using different modes (shared, exclusive…). Choosing a mode instead of another to access a given resource in a session will either let other sessions (or transaction) access the same resource or will make other sessions wait for that resource to be unlocked. Let’s notice that all locking modes are not compatible. For that reason, Microsoft provided a documentation page about what they call lock compatibility.
Still, intuitively, we could say that a deadlock falls into the second case, the one that tells other sessions to wait for a resource, but this wait might never end. This second case is commonly referred to as “blocking”. We will take some time to understand blocking before talking about deadlocks as they seem to be the worst case of blocking
Understanding blocking
A blocking situation can be understood with the following example.
UserA is currently editing an invoice, which implies an UPDATE statement against an Invoice table with a WHERE clause that restricts to a particular value of InvoiceId column of that table. To perform this operation, the thread associated to that session inside SQL Server database engine has to acquire and hold:
At the same time, UserB wants to get a list of the invoices for current month and unfortunately, the invoice UserA is editing sits in that list. UserB ’s thread will:
The situation can be graphically summarized as follows:
This situation will end as soon as the UPDATE query has been completed and UserA has committed their transaction.
As we may expect, we can encounter a lot more complex situations, involving a session holding multiple locks on multiple resources. However, when blocking occurs, using the appropriate query, we will be able to get a tree view of blocking like the following one:
In this example, we would pinpoint three blocking sessions (59, 79, 145) but as the session with id 145 is actually blocked by the session with id 59, there are actually two “top blocking sessions” (59 and 79). These are called “head blockers” while the other sessions are called “waiters”.
Understanding deadlocks
Although it’s based on the same principles, deadlocks are different from blocking. Actually, when a deadlock situation happens, there is no identifiable head blocker as both sessions implied hold incompatible locks on objects the other session needs to access. It’s a circular blocking chain.
For better understanding, we will go back to the situation we used for blocking presentation and add some complexity to that situation.
Let’s say that in order to modify a row in Invoice table, UserA must also read from an InvoiceDetails table to get the total that is billed to customer. Let’s say that, no matter the reason, UserB has already acquired an exclusive lock on a page containing a row of InvoiceDetails table that UserA needs to read.
In such a case, we are in the situation depicted by following figure. (As a reminder, green is used to refer to UserA and orange for UserB )
As you can see in the figure above, both threads are waiting for a lock that won’t be ever released as the activity of one is suspended until the other releases its acquired locks. There can be more complicated in real-life situations and I would suggest those interested in the subject to search the web for resources like the one written by Minette Steynberg in 2016 entitled What is a SQL Server deadlock?.
Fortunately, the SQL Server database engine comes with a deadlock monitor thread that will periodically check for deadlock situations, choose one of the processes implied as a victim for termination. While this is a good point for one of the sessions, this is not for the other. The “victim” is actually terminated with an error and has to be run again.
Here is some further information about the deadlock monitor thread:
Once the deadlock victim is chosen, it will roll back the transaction of this victim and return a 1205 error message to the user. The error message looks like follows
Transaction (Process ID 89) was deadlocked on resources with another process and has been chosen as the deadlock victim. Rerun the transaction.
Deadlock in action
In this section, we will implement the example explained above in T-SQL and check that the explanation corresponds to what actually happens in the real world.
SQLShack
SQL Server deadlock definition and Overview
Introduction
In this series, I will provide all of the information you need to understand in order to deal with deadlocks.
In part 1 (this article) I will explain:
Deadlock Definition
A deadlock occurs when 2 processes are competing for exclusive access to a resource but is unable to obtain exclusive access to it because the other process is preventing it. This results in a standoff where neither process can proceed. The only way out of a deadlock is for one of the processes to be terminated. SQL Server automatically detects when deadlocks have occurred and takes action by killing one of the processes known as the victim.
Deadlocks do not only occur on locks, from SQL Server 2012 onward, deadlocks can also happen with memory, MARS (Multiple Active Result Sets) resources, worker threads and resources related to parallel query execution.
How do I know if I have a deadlock?
The first sign you will have of a deadlock is the following error message which will be displayed to the user who own the process that was selected as the deadlock victim.
Msg 1205, Level 13, State 51, Line 6
Transaction (Process ID 62) was deadlocked on lock resources with another process and has been chosen as the deadlock victim. Rerun the transaction.
The other user whose process was not selected as the victim will be most likely be completely unaware that their process participated in a deadlock.
Deadlocks definitions types
There are 2 different types of deadlocks.
Cycle locks deadlock definition
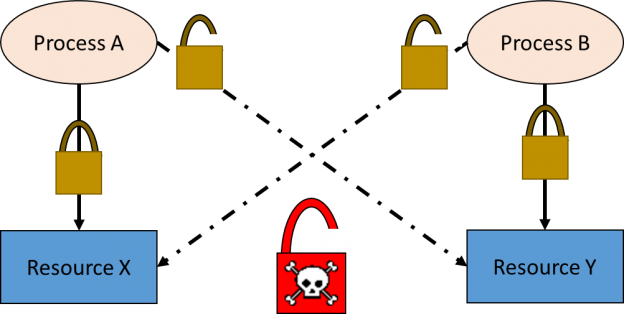
A cycle deadlock is what happens when a process A which is holding a lock on resource X is waiting to obtain an exclusive lock on resource Y, while at the same time process B is holding a lock on resource Y and is waiting to obtain an exclusive lock on resource X.

Figure 1: Image of a cycle lock
Conversion locks deadlock definition
A conversion deadlock occurs when a thread tries to convert a lock from one type to another exclusive type but is unable to do so because another thread is already also holding a shared lock on the same resource.
There are 3 types of conversions locks in SQL Server.
| Type | Name | Description |
| SIU | Share with Intent Update | The thread holds some shared locks but also has update locks on some components (page or row). |
| SIX | Share with Intent Exclusive | The thread has both a shared lock and an exclusive lock on some components (page or row). |
| UIX | Update with Intent Exclusive | Both a U lock and an IX lock are taken separately but held at the same time. |
How SQL Server handles deadlocks
The lock manager in SQL Server automatically searches for deadlocks, this thread which is called the LOCK_MONITOR looks for deadlocks every 5 seconds. It looks at all waiting locks to determine if there are any cycles. When it detects a deadlock it chooses one of the transactions to be the victim and sends a 1205 error to the client which owns the connection. This transaction is then terminated and rolled back which releases all the resources on which it held a lock, allowing the other transaction involved in the deadlock to continue.
If there are a lot of deadlocks SQL Server automatically adjusts the frequency of the deadlock search, and back up to 5 seconds if deadlocks are no longer as frequent.
How does SQL Server choose the victim?
There are a couple of factors that come into play here. The first is the deadlock priority. The deadlock priority of a transaction can be set using the following command:
How to fix SQL Server deadlocks
By Grant Fritchey
The first time a user sees the following message, the result of an unhandled deadlock error in SQL Server, it can come as quite a shock.
Msg 1205, Level 13, State 56, Line 10
Transaction (Process ID 62) was deadlocked on lock resources with another process and has been chosen as the deadlock victim. Rerun the transaction.
Two or more sessions were waiting to acquire a lock on a resource already locked by another session in the same locking chain. The result is a ‘circular chain’ where no session can complete, and so SQL Server is forced to intervene to clear up the mess. It automatically chooses one of the sessions as the ‘victim’, kills it and rolls back its transaction. It means that the other sessions may proceed, but that is little comfort to the hapless victim, and if that victim happens to be a session running a critical business process, then it may soon be of little comfort to the DBA.
Handling deadlock errors
Ideally, no user should ever be confronted with error message 1205, even if a deadlock does occur. Any application code that issues database queries should be equipped with error handling that deals with the problem gracefully, and sends the calling client a «user friendly» message. It should also have retry logic that allows the victim transaction to rerun, once the deadlock clears.
Nevertheless, deadlock errors cause resource contention, disruption and delay, and cannot be ignored. DBAs must know immediately when one occurs, by alerting on 1205 errors, and then need at their fingertips all of the information necessary to troubleshoot the deadlock and ensure that it doesn’t recur.
Resolving deadlocks with SQL Server performance monitoring
If you suspect deadlocks are occurring on your SQL Server instances, what can you do? We’ll review three approaches to their detection and resolution, each of which involves retrieving from SQL Server the information describing the deadlock, namely the deadlock graph. This reveals the deadlocked sessions, what statements were being run, the database, objects and pages on which the sessions were deadlocked, and more.
Traceflag 1222 – Method 1
There was a time, when they only way to get the deadlock graph was to enable traceflag 1222 (or 1204 on SQL 2000) to capture it into the error log. Figure 1 shows the error log contents, highlighting the process selected as the deadlock victim then above it the deadlock graph output.

Figure 1 – the error log, with the victim of a deadlocked process highlighted in red
However, unless you have the traceflag enabled permanently, you’d need to enable it and wait for the deadlock to recur. As you can see, SQL Server fills the error log with a lot of information, and there is also a lot of manual work for the DBA still to do here, in working out the sessions and resources (tables, indexes) involved in the deadlock. Only use this technique if you have no other choice. With SQL Server 2008 and later there are much better ways.
Extended Events – Method 2
On SQL Server 2008 or later, the system_health extended event session is enabled by default, and automatically captures the deadlock graph. You can retrieve it retrospectively, in response to a 1205 error alert, either by running a T-SQL/XPath query (e.g. see Listing 1 of Gail Shaw’s article), or using the Extended Events UI target data viewer in SSMS (SQL Server 2012 and later only), as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2 – View Target Data from the SQL Server Management Studio UI
There may be thousands of events displayed, but right-click on the data viewer and select Filter by this Value (or use the Extended Events | Filter menu) to set up a filter on the name column so the viewer displays an event only if it «Contains» the value «deadlock«.
By clicking on an xml_deadlock_report event in the data viewer, we can see the deadlock graph, either as XML (Details tab) or in graphical form (Deadlock tab).

Figure 3 – an XML deadlock report
This approach is better than using traceflags but it still requires the DBA to be adept at reading XML deadlock graphs (the graphical output ‘hides’ too much information), and it still misses the full picture of what was happening on the server at the time the deadlock occurred. Was the problem exacerbated because the server under CPU or IO or memory pressure at the time? What other concurrent activity was occurring on the server?
SQL Monitor – Method 3
A SQL Server performance monitoring tool such as SQL Monitor aims to give the DBA enough information to resolve a deadlock, without wading too deep into an XML deadlock graph, and places this information within the context of the overall pattern of activity on the server at the time. Not only does this ease the process of troubleshooting the deadlock, it also makes performance troubleshooting overall much more effective.
It detects a deadlock automatically and raises an alert, emailed to your inbox. The top half of the Details tab, on the alert screen in SQL Monitor, presents in a digestible form the sessions, queries and database objects involved in the deadlock.

Figure 4 – a deadlocked process in SQL Monitor, Redgate’s SQL Server performance monitoring tool
This may well be all the information you need, but the Output tab of this screen still reveals the full XML deadlock graph, if required.
As well as seeing information about the processes involved, SQL Monitor provides context about what was going on at that point in time. The lower half of the screen shows performance counter data, running machine processes and their resource consumption, expensive queries, as well as the waits relating to them. The line on the graphs indicates the time the deadlock occurred.

Figure 5 – SQL Monitor’s performance data graphs
The Top queries tab will reveal the plan handle for the statements involved in the deadlock, so you can retrieve their execution plans, should query tuning be required in order to resolve the problem (which it often is!).
Possible solutions in this case include rewriting the transactions so that they access tables in the same order, or perhaps running the transactions using either the READ COMMITTED SNAPSHOT or SNAPSHOT isolation level, where readers don’t take Shared locks.
Summary
Checking error logs for deadlock information is an outdated and time-consuming way to troubleshoot the problem. A tool such as Extended Events can help the DBA resolve deadlocks, but it still requires additional work to set up alerting, as well as a series of other SQL Server performance monitoring resources and reports to gather the required performance metrics.
A SQL Server performance monitoring tool like SQL Monitor enables a DBA to shift focus from diagnostic data collection and management to problem-solving based on alerts that supply sufficient information to resolve the deadlock quickly, and offer a richer understanding of server activity at the time of the problem.
Monitoring the activity and performance of SQL Server and resolving problems is time-consuming
That’s where SQL Monitor steps in with clear insights into SQL Server performance in real time, bringing problems to your attention before anyone else notices.
With its embedded expertise from SQL Server experts and MVPs, it gives you the data and advice you need to find and fix issues before users are even aware.
So, whether you’re looking for baselining, wait stats, expensive queries, or instant alerts, find out how SQL Monitor gives you everything you need – and more – with a free 14 day trial.
Got a question?
If you’d like any help, or have any questions about our tools and purchasing options, please get in touch.
Get started with SQL Monitor
SQL Monitor is part of the SQL Toolbelt
Secure your backups and make deployment safe, with the industry-standard products for SQL Server development, deployment, backup, and monitoring.